What Is The Principle Of Hydraulic Control Of Degree Rotating Hydraulic Tilt Ditching Bucket?
In the world of construction and excavation, efficiency and precision are paramount. One tool that has revolutionized these industries is the degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching bucket. This innovative attachment has become an indispensable part of many construction projects, offering unparalleled flexibility and control. But have you ever wondered how this piece of machinery works? In this article, we'll delve into the principles behind the hydraulic control of the degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching bucket, exploring its composition, operation, and the technology that makes it so effective.
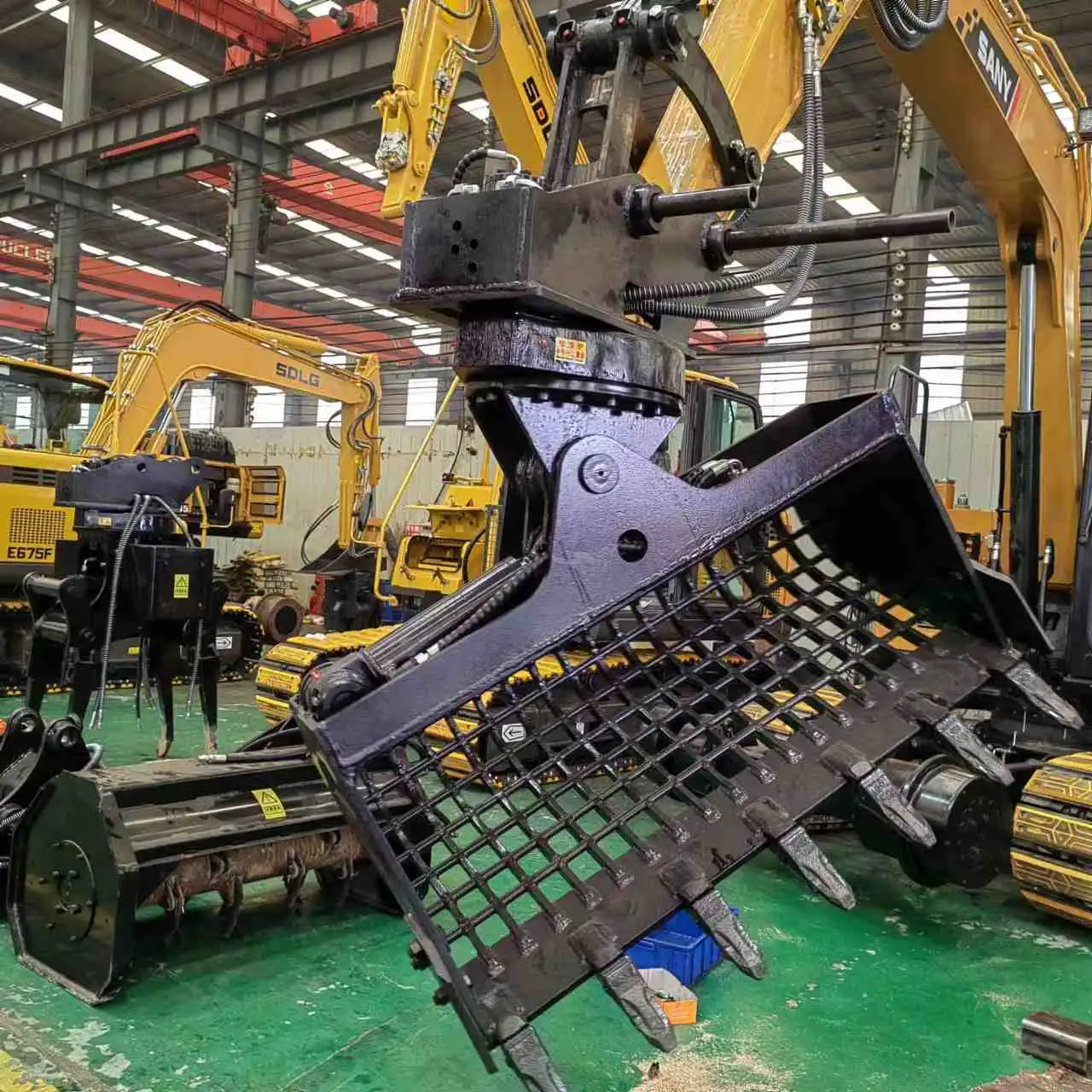

Composition Of The Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system of a degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching bucket is a sophisticated and highly engineered assembly, carefully designed to deliver exceptional performance, precision, and durability. Comprising several key components that work in unison, the system ensures smooth operation and responsive control of the bucket's various movements. These components include the hydraulic pump, control valves, hydraulic cylinders, and an intricate network of hoses and fittings that allow for the effective distribution of hydraulic fluid.
At the heart of the hydraulic system is the hydraulic pump, which is typically powered by the excavator's engine. This pump generates the necessary pressure to propel hydraulic fluid throughout the system. The fluid is pressurized and then channeled to the various components of the system, where its flow and direction are precisely controlled. The hydraulic pump is a critical element of the system, as its efficiency directly impacts the overall performance of the bucket’s hydraulic functions.
Once the hydraulic fluid is pressurized, it travels through a series of control valves, which serve as the command center of the hydraulic system. These valves are responsible for regulating the flow and direction of the hydraulic fluid, determining the movements and positioning of the bucket. The ability to finely adjust these valves allows operators to control the bucket’s rotation, tilt, and sometimes even extension or retraction, ensuring precise operation in a variety of working conditions. The control valves act as the interface between the operator’s commands and the hydraulic actions performed by the bucket.
The hydraulic cylinders, often referred to as the "muscles" of the system, play an essential role in translating hydraulic pressure into mechanical movement. These cylinders are responsible for the tilting and rotating actions of the bucket, as well as any other movements, such as extending or retracting the bucket when necessary. In a degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching bucket, multiple cylinders are typically used, each serving a specific function to provide coordinated and precise control. These cylinders are robustly designed to withstand high pressures and provide consistent, reliable performance under demanding conditions.
All of these components—pump, valves, cylinders—are interconnected through a carefully engineered network of high-pressure hoses and fittings. This network is crucial to the effective distribution of hydraulic fluid, ensuring that each part of the system receives the correct amount of fluid at the right pressure. The hoses and fittings must be capable of withstanding the intense pressures generated by the hydraulic pump while also providing the flexibility required for the movement of a rotating and tilting bucket. The design of this network is vital for maintaining consistent fluid flow, reducing friction, and ensuring the system operates smoothly without leaks or blockages.
Hydraulic Control Of The Tilt Bucket
The hydraulic control system of the tilt function in a degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching bucket exemplifies the precision engineering that goes into these advanced attachments. This system is designed to offer fine control and accurate movement of the bucket, ensuring that operators can perform tasks with exceptional precision, even in complex and demanding environments.
The tilting action is driven by a well-coordinated hydraulic system that uses dedicated tilt cylinders to manipulate the bucket's position. When the operator activates the tilt function, the control valve directs pressurized hydraulic fluid into one side of the tilt cylinder, while simultaneously allowing fluid to exit from the opposite side. This pressure differential causes the cylinder’s rod to either extend or retract, depending on the direction of the fluid flow, which in turn tilts the bucket forward or backward. The level of tilt can be finely adjusted by regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid, allowing for precise positioning of the bucket to meet the specific requirements of the task.
This sophisticated system offers significant control over the bucket’s tilt angle, providing operators with the flexibility to perform tasks such as grading, backfilling, or precise material placement with high accuracy. The ability to adjust the tilt angle ensures that the operator can maintain the desired grade or slope, even on uneven surfaces, making the bucket ideal for a wide range of applications.
What truly sets the degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching bucket apart from traditional buckets is its unique ability to combine the tilting function with rotation. This combination is achieved through an additional hydraulic circuit that operates a rotary actuator or a set of hydraulic cylinders specifically designed to provide rotational movement. The integration of tilt and rotation allows the bucket to be positioned at virtually any angle, offering a high level of versatility for the excavator. Operators can rotate the bucket to move material across different areas, and simultaneously adjust the tilt to control material flow, giving them the ability to work in tight spaces and around obstacles with ease.
The synergy between the tilting and rotating actions maximizes the bucket’s versatility, allowing operators to accomplish a wider range of tasks without needing to reposition the excavator. Whether it’s for backfilling around infrastructure, digging ditches, or leveling material, this combined functionality ensures that the bucket can be positioned for maximum efficiency and precision, saving time and increasing productivity.
Angle Monitoring And Control
One of the most advanced features of modern degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching buckets is their sophisticated angle monitoring and control systems. These systems provide real-time feedback to the operator, allowing for unprecedented precision in bucket positioning.
At the heart of this system are angle sensors, often in the form of inclinometers or rotary encoders. These sensors continuously monitor the tilt and rotation angles of the bucket, sending this data to a central control unit. The control unit processes this information and displays it to the operator through a user-friendly interface, typically integrated into the excavator's cab display.
Advanced systems go a step further by incorporating automated angle control. This feature allows operators to preset specific angles or positions, and the hydraulic system will automatically adjust to achieve and maintain these settings. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces operator fatigue, especially in jobs that require repetitive positioning.
Some cutting-edge degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching buckets even integrate with GPS and machine control systems. This integration allows for even greater precision, enabling the bucket to automatically adjust its position based on 3D terrain models or predefined work plans. This level of automation is particularly valuable in large-scale earthmoving projects or in applications where precise grading is critical.
In conclusion, the degree rotating hydraulic tilt ditching bucket represents a pinnacle of hydraulic engineering in construction equipment. Its sophisticated hydraulic control system, combining precise tilt and rotation capabilities with advanced angle monitoring and control, offers unparalleled versatility and efficiency. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovations in this field, further enhancing the capabilities of these essential construction tools. Whether you're involved in construction, excavation, or are simply fascinated by hydraulic engineering, understanding the principles behind these remarkable attachments provides valuable insight into the technology shaping our built environment.
Contact Information
References:
[1] Hydraulic Systems: Components and Functions. Fluid Power Journal. (2021)
[2] Advanced Hydraulic Control Systems in Construction Equipment. Construction Equipment Magazine. (2022)
[3] Precision Earth Moving: The Role of GPS and Machine Control in Modern Excavation. Engineering News-Record. (2023)