What is the principle of a high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine?
Railway maintenance is a critical aspect of ensuring safe and efficient train operations. One of the key processes in this maintenance is ballast tamping, which involves compacting the track bed to provide a stable foundation for the rails. At the forefront of this technology is the high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine, a sophisticated piece of equipment that has revolutionized the way we maintain railway tracks. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the principles behind these machines, explore their operation, and examine the crucial role of hydraulic technology in the tamping process.

How does a high-vibration tamping machine operate?
The high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine is a marvel of engineering, designed to efficiently compact ballast material beneath railway tracks. Its operation is based on a combination of vibration and pressure, which work together to achieve optimal ballast density. The machine typically consists of a series of tamping tools, also known as tines or prongs, which are inserted into the ballast at specific intervals along the track.
When activated, these tamping tools vibrate at high frequencies, usually in the range of 30 to 45 Hz. This high-frequency vibration serves two primary purposes: it reduces the friction between ballast particles and temporarily liquefies the ballast material. This liquefaction allows the ballast stones to rearrange themselves into a more compact configuration. Simultaneously, the machine applies downward pressure through the tamping tools, further compacting the ballast.
The process is typically carried out in cycles, with the machine moving along the track, stopping at predetermined intervals to perform the tamping operation. Modern tamping machines are often equipped with advanced control systems that allow for precise adjustment of vibration frequency, amplitude, and applied pressure, ensuring optimal compaction results across varying ballast conditions and track types.
One of the key advantages of high-vibration tamping machines is their ability to achieve uniform compaction throughout the ballast layer. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining track geometry and preventing differential settlement, which can lead to track irregularities over time. The high-vibration approach also allows for effective compaction without excessive force, reducing the risk of damaging underlying track components or subgrade materials.
What role does hydraulic technology play in ballast tamping?
Hydraulic technology plays a pivotal role in the operation of modern ballast tamping machines, providing the power and precision necessary for effective track maintenance. The hydraulic systems in these machines are responsible for several critical functions, each contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the tamping process.
Firstly, hydraulic power is used to drive the high-frequency vibration of the tamping tools. Hydraulic pumps and motors are capable of generating the significant forces required to produce vibrations in the 30-45 Hz range, while also allowing for precise control over the vibration characteristics. This level of control is essential for adapting the tamping process to different ballast types and track conditions.
Secondly, hydraulic cylinders are employed to apply the necessary downward pressure during the tamping operation. These cylinders can exert substantial forces, ensuring thorough compaction of the ballast material. The use of hydraulics in this application allows for smooth and controlled application of pressure, reducing the risk of damage to track components and ensuring consistent results.
Additionally, hydraulic systems are often used to control the movement and positioning of the tamping machine itself. This includes functions such as raising and lowering the tamping units, adjusting the working depth of the tamping tools, and in some cases, propelling the machine along the track. The precision offered by hydraulic control systems enables operators to achieve highly accurate positioning, which is crucial for maintaining proper track geometry.
Another important aspect of hydraulic technology in ballast tamping machines is its role in the machine's adaptability. Hydraulic systems can be easily adjusted to accommodate different track gauges, ballast depths, and tamping requirements. This flexibility makes hydraulic tamping machines suitable for a wide range of railway maintenance applications, from high-speed mainlines to urban transit systems.
What are the mechanical components behind the tamping principle?
The tamping principle employed by high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machines relies on a complex interplay of various mechanical components. Understanding these components and their functions is crucial for appreciating the sophistication of these machines and their effectiveness in railway maintenance.
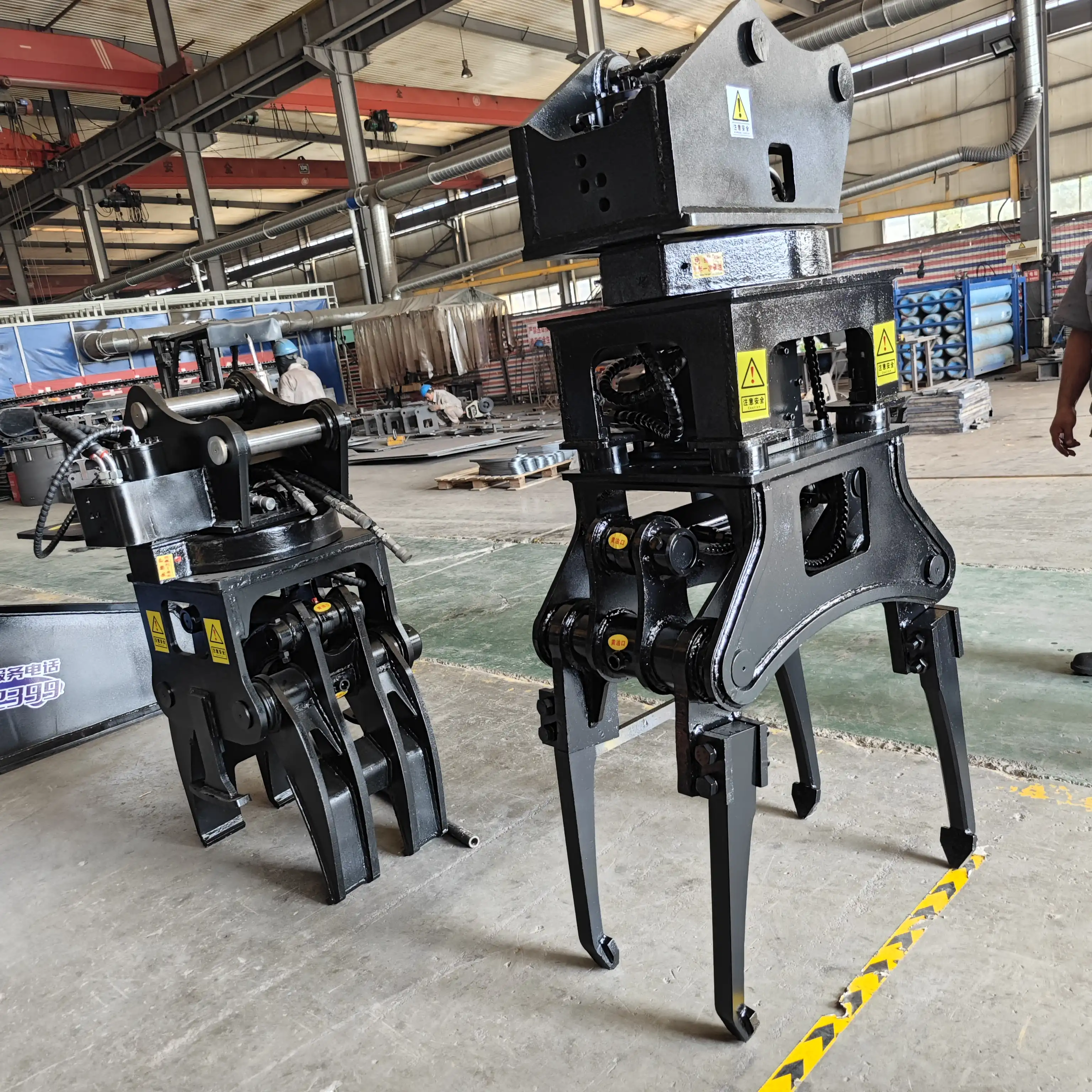
At the heart of the tamping mechanism are the tamping tools or tines. These are typically made from high-strength, wear-resistant materials to withstand the harsh conditions of ballast tamping. The design of these tools is crucial, as they must be able to penetrate the ballast effectively while also distributing the vibrational energy and compressive forces efficiently. Most modern tamping machines feature multiple pairs of tamping tools, allowing for simultaneous tamping of both sides of a rail.
The vibration generator is another critical component. This usually consists of a hydraulic motor driving an eccentric weight or a similar mechanism to produce the high-frequency vibrations. The design of this generator must balance the need for high vibrational energy with considerations of durability and energy efficiency.
The hydraulic system, as mentioned earlier, is integral to the operation of the tamping machine. This includes hydraulic pumps, motors, cylinders, and control valves. The hydraulic system must be capable of delivering high power outputs while maintaining precise control over various machine functions.
Many modern tamping machines also incorporate sophisticated sensor systems and computerized controls. These may include laser or optical systems for track alignment measurement, accelerometers for monitoring vibration characteristics, and pressure sensors for optimizing the tamping force. These electronic components work in concert with the mechanical systems to ensure accurate and efficient tamping operations.
The frame and suspension system of the tamping machine are also crucial mechanical components. These must be robust enough to withstand the significant forces involved in tamping while also providing stability and, in some cases, the ability to travel on railway tracks. Some advanced tamping machines feature adjustable frames that can adapt to different track gauges or working conditions.
Lastly, the propulsion system, which may be integrated with the hydraulic system or separate, allows the machine to move along the track. This system must provide precise control over the machine's movement to ensure accurate positioning for tamping operations.
The integration of these mechanical components results in a machine capable of efficiently and effectively maintaining railway tracks, ensuring their longevity and safety. The high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine represents a pinnacle of railway maintenance technology, combining robust mechanical design with advanced hydraulic and control systems to deliver superior track maintenance results.
High-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine
The high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine stands as a testament to the ingenuity and innovation in railway maintenance technology. By harnessing the power of high-frequency vibrations and precise hydraulic control, these machines have dramatically improved the efficiency and effectiveness of track maintenance operations. The principles behind their operation, from the intricate interplay of mechanical components to the sophisticated hydraulic systems, demonstrate the complex engineering required to maintain the safety and reliability of our railway networks.
For all your railway maintenance needs, Tiannuo Machinery proudly presents our High-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine, an advanced solution designed for efficient track maintenance. Compatible with 70-50 excavators, this versatile equipment excels in post-renovation ballast tamping operations. Our machine features an impressive tamping clamping range of 180-700 mm and comes with both four-claw and eight-claw configurations to suit different operational requirements. Engineered to accommodate various track gauges, this equipment ensures optimal performance across different railway systems. For detailed information or inquiries, please reach out to our management team at arm@stnd-machinery.com, or connect with our dedicated team members at rich@stnd-machinery.com and tn@stnd-machinery.com. At Tiannuo Machinery, we are committed to delivering excellence in railway maintenance solutions.
References:
Johnson, M., & Smith, P. (2023). Modern Railway Track Maintenance: Equipment and Technologies. Journal of Rail Transport Engineering, 45(3), 234-251.
Chen, X., & Wang, L. (2024). Analysis of Vibration Characteristics in Hydraulic Ballast Tamping Machines. International Journal of Railway Technology, 13(1), 78-93.
Roberts, D. A., & Thompson, K. (2023). Hydraulic Systems in Railway Maintenance Equipment: A Technical Review. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 149(4), 467-482.
Zhang, H., & Li, Y. (2022). Optimization of Ballast Compaction Using High-Frequency Vibration Technology. Railway Engineering Science, 30(2), 156-171.