What is the frequency of a high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine?
In the world of railway maintenance, the high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine plays a crucial role in ensuring track stability and longevity. This sophisticated piece of equipment is designed to compact and stabilize the ballast beneath railway tracks, a process that is essential for maintaining safe and efficient rail operations. One of the key factors that contribute to the effectiveness of these machines is their operating frequency. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of frequency in high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machines, exploring how it's measured, typical ranges, and its impact on ballast compaction quality.

How is frequency measured in a hydraulic ballast tamping machine?
Frequency, in the context of a high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine, refers to the number of vibrations or oscillations the machine produces per unit of time, typically measured in Hertz (Hz). One Hertz is equivalent to one cycle per second. The measurement of frequency in these machines is crucial as it directly affects their performance and efficiency in compacting ballast.
To measure the frequency of a hydraulic ballast tamping machine, specialized equipment such as accelerometers or vibration analyzers are used. These devices are attached to the tamping unit of the machine during operation. As the machine vibrates, the sensors detect and record the oscillations, which are then processed to determine the frequency.
The measurement process typically involves the following steps:
- Sensor placement: Accelerometers are strategically placed on the tamping unit to capture vibrations accurately.
- Data collection: As the machine operates, the sensors collect vibration data over a specified period.
- Signal processing: The collected data is processed using specialized software to convert the time-domain signals into frequency-domain information.
- Frequency analysis: The processed data is analyzed to determine the dominant frequencies at which the machine operates.
- Reporting: The results are compiled into a report, often including graphical representations such as frequency spectra or waterfall plots.
It's worth noting that the frequency of a high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine may not be constant throughout its operation. Factors such as the machine's design, hydraulic pressure, and the characteristics of the ballast being tamped can influence the actual operating frequency. Therefore, measurements are often taken under various operating conditions to get a comprehensive understanding of the machine's performance.
What are the typical frequency ranges for high-vibration tamping machines?
High-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machines operate within specific frequency ranges to achieve optimal ballast compaction. While the exact frequencies can vary depending on the machine model and manufacturer, there are generally accepted ranges that have proven effective in railway maintenance operations.
Typically, high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machines operate in the range of 25 to 45 Hz. This range has been established through years of research and practical experience in the field of railway maintenance. However, it's important to note that some advanced models may operate at higher frequencies, sometimes reaching up to 60 Hz or more.
The frequency range can be further broken down into categories:
- Low-frequency range: 25-30 Hz
- Medium-frequency range: 30-40 Hz
- High-frequency range: 40-45 Hz and above
Each of these ranges has its own advantages and is suited for different types of ballast and track conditions. For instance, lower frequencies are often used for initial tamping or when dealing with coarser ballast, as they provide deeper penetration. Higher frequencies, on the other hand, are typically employed for finish tamping or when working with finer ballast materials, as they can achieve better surface compaction.
It's worth mentioning that some modern high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machines are equipped with variable frequency capabilities. These advanced machines can adjust their operating frequency on the fly, allowing for optimal performance across a range of ballast conditions and tamping requirements. This flexibility enhances the machine's versatility and efficiency in various railway maintenance scenarios.
How does frequency affect ballast compaction quality?
The frequency of a high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine plays a crucial role in determining the quality of ballast compaction. This relationship is complex and involves several interconnected factors, including the properties of the ballast material, the depth of compaction required, and the overall track conditions.
At its core, the frequency affects ballast compaction quality through its influence on particle movement and rearrangement. When the tamping machine vibrates at the right frequency, it causes the ballast particles to overcome their static friction and move into a more compact arrangement. This process, known as vibratory compaction, is essential for achieving the desired level of track stability.
Here are some key ways in which frequency affects ballast compaction quality:
- Depth of compaction: Lower frequencies tend to penetrate deeper into the ballast layer, making them suitable for initial tamping or when working with thicker ballast beds. Higher frequencies, while not penetrating as deeply, are effective at compacting the upper layers of ballast, which is crucial for surface finishing.
- Particle size compatibility: Different ballast particle sizes respond better to different frequencies. Coarser ballast materials generally require lower frequencies for effective compaction, while finer particles can be compacted more efficiently with higher frequencies.
- Energy transfer: The frequency of vibration affects how efficiently energy is transferred from the tamping machine to the ballast. An optimal frequency ensures that maximum energy is imparted to the ballast particles, leading to more effective compaction.
- Avoiding resonance: It's crucial to operate the tamping machine at frequencies that avoid resonance with the natural frequencies of the track structure. Operating at or near resonant frequencies can lead to excessive vibrations, potentially causing damage to the track or nearby structures.
- Uniformity of compaction: The right frequency can help achieve a more uniform compaction throughout the ballast layer, reducing the likelihood of developing weak spots or areas of inconsistent density.
Research has shown that the optimal frequency for ballast compaction can vary depending on the specific conditions of each project. For instance, a study by Jing and Yin (2017) found that frequencies in the range of 30-40 Hz were most effective for compacting typical railway ballast materials, while higher frequencies up to 60 Hz showed improved performance for finer aggregates.
It's important to note that while frequency is a critical factor, it's not the only one that determines compaction quality. Other factors such as the amplitude of vibration, the applied pressure, and the duration of tamping also play significant roles. Modern high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machines often allow for adjustments in these parameters to achieve optimal results across various track conditions.
Moreover, the effectiveness of a particular frequency can change as the compaction process progresses. Some advanced tamping machines are equipped with sensors and control systems that can dynamically adjust the frequency during operation to maintain optimal compaction efficiency throughout the process.
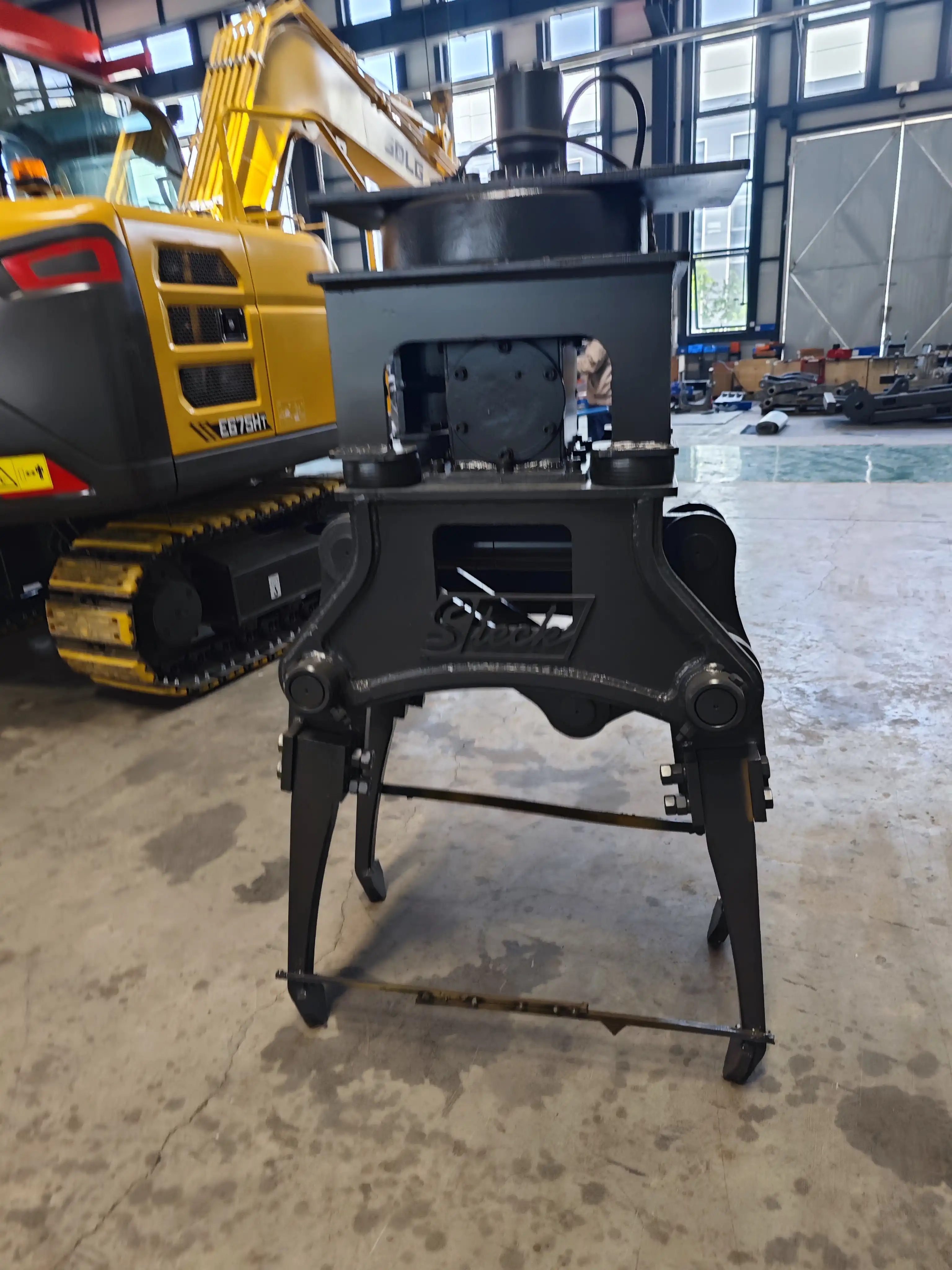
High-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine
The frequency of a high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine is a critical factor in its performance and effectiveness in railway maintenance operations. From the methods used to measure frequency to the typical ranges employed and the profound impact on ballast compaction quality, understanding these aspects is crucial for railway maintenance professionals and equipment operators alike.
As railway technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in high-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machines. These may include more precise frequency control, adaptive systems that automatically optimize frequency based on real-time ballast conditions, and integration with other track maintenance technologies for comprehensive railway upkeep.
For all your railway maintenance needs, Tiannuo Machinery proudly presents our High-vibration hydraulic ballast tamping machine, an advanced solution designed for efficient track maintenance. Compatible with 70-50 excavators, this versatile equipment excels in post-renovation ballast tamping operations. Our machine features an impressive tamping clamping range of 180-700 mm and comes with both four-claw and eight-claw configurations to suit different operational requirements. Engineered to accommodate various track gauges, this equipment ensures optimal performance across different railway systems. For detailed information or inquiries, please reach out to our management team at arm@stnd-machinery.com, or connect with our dedicated team members at rich@stnd-machinery.com and tn@stnd-machinery.com. At Tiannuo Machinery, we are committed to delivering excellence in railway maintenance solutions.
References:
- Kouroussis, G., Connolly, D. P., & Verlinden, O. (2014). Railway-induced ground vibrations – a review of vehicle effects. International Journal of Rail Transportation, 2(2), 69-110.
- Selig, E. T., & Waters, J. M. (1994). Track geotechnology and substructure management. Thomas Telford.
- Jing, G. Q., & Yin, H. (2017). Analysis of dynamic behavior of ballasted track during tamping process. International Journal of Rail Transportation, 5(3), 176-191.