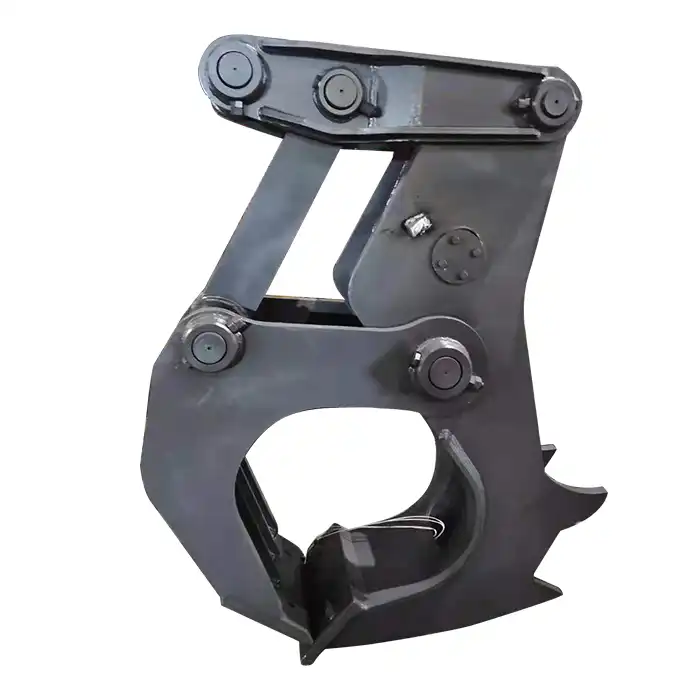
What sizes of logs can the excavator wood splitter handle?
Excavator wood splitters, also known as hydraulic log splitters or excavator-mounted log splitters, are designed to tackle a wide range of log sizes. However, the exact dimensions they can handle depend on several factors, including the specific model, the power of the excavator it's attached to, and the type of wood being split. Generally speaking, most wood splitters can handle logs with diameters ranging from 10 inches to 36 inches, and lengths up to 20 feet or more.

It's important to note that while these machines are incredibly versatile, they do have their limits. Attempting to split logs that exceed the manufacturer's recommended size can lead to equipment damage, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards. Therefore, it's crucial to understand the capabilities of your specific excavator wood splitter and use it accordingly.
Maximum Log Diameter And Length Capacities Of Wood Splitters
The maximum log diameter and length that an excavator wood splitter can handle varies depending on the model and specifications. Here's a general overview of what you can expect:
Log Diameter: Most standard wood splitters can handle logs with diameters ranging from 10 to 24 inches. However, heavy-duty models are capable of splitting logs up to 36 inches in diameter or even larger. It's worth noting that the splitting force required increases exponentially with the log diameter, so larger logs will require more powerful splitters.
Log Length: When it comes to length, wood splitters are quite flexible. Many models can accommodate logs up to 20 feet long, with some specialized units capable of handling even longer pieces. The length capacity is often more dependent on the excavator's reach and the operator's skill than on the splitter itself.
For instance, a mid-range excavator wood splitter might have the following specifications:
- Maximum log diameter: 24 inches
- Maximum log length: 16 feet
- Splitting force: 30 tons
However, it's important to remember that these are just examples, and actual capacities can vary significantly between different models and manufacturers. Always refer to the specific product specifications when choosing an excavator wood splitter for your needs.
Splitting Tough VS. Softwood Logs: What to expect
The type of wood being split plays a crucial role in determining the performance and capacity of an excavator wood splitter. Different wood species have varying densities, grain structures, and moisture contents, all of which affect how easily they can be split.
Softwoods: Softwood species, such as pine, spruce, and cedar, are generally easier to split. These woods typically have straight grains and fewer knots, allowing the splitter to work through them with less resistance. When dealing with softwoods, an excavator wood splitter can often handle logs at the upper end of its diameter capacity without much difficulty.
Hardwoods: Hardwood species like oak, maple, and hickory present more of a challenge. These woods are denser, often have more complex grain patterns, and can contain more knots. As a result, they require more force to split and may necessitate multiple passes through the splitter, especially for larger diameter logs.
When splitting tough hardwoods, you might need to:
- Use a more powerful excavator wood splitter
- Reduce the maximum log diameter you attempt to split
- Allow for longer processing times
- Consider pre-splitting very large logs with a chainsaw before using the splitter
It's also worth noting that the moisture content of the wood can affect splitting performance. Freshly cut "green" wood is often easier to split than dried wood, as the fibers are more pliable. However, very wet wood can be heavier and more challenging to handle.
Case studies: Real-world examples of log splitting capabilities
To better understand the practical capabilities of excavator wood splitters, let's look at some real-world examples:
Case Study 1: Forestry Operation in Oregon
A large-scale forestry operation in Oregon used a high-capacity wood splitter to process Douglas fir logs. The splitter, mounted on a 30-ton excavator, was capable of handling logs up to 36 inches in diameter and 20 feet in length. Over a month-long period, the team processed over 1,000 logs, with an average diameter of 28 inches. The splitter's efficiency allowed them to increase their output by 40% compared to their previous method.
Case Study 2: Firewood Business in Michigan
A small firewood business in Michigan invested in a mid-range excavator wood splitter for their operation. This splitter, designed to handle logs up to 24 inches in diameter, was used primarily for processing hardwoods like oak and maple. The business owner reported being able to split logs up to 22 inches in diameter consistently, with occasional success on slightly larger pieces. The addition of the wood splitter allowed them to double their daily firewood production.
Case Study 3: Land Clearing Project in Texas
A land clearing project in Texas utilized a wood splitter to process a variety of wood types, including both softwoods and hardwoods. The team found that while their splitter was rated for logs up to 30 inches in diameter, they achieved the best results when limiting hardwood logs to 24 inches or less. For softwoods, they were able to consistently split logs up to the full 30-inch capacity. The versatility of the excavator wood splitter allowed them to efficiently process all the cleared timber on-site, significantly reducing waste and transportation costs.
These case studies demonstrate the versatility and efficiency of excavator wood splitters in various applications. While the exact capabilities can vary, these machines consistently prove their worth in handling a wide range of log sizes and types.
Excavator Wood Splitter For Sale
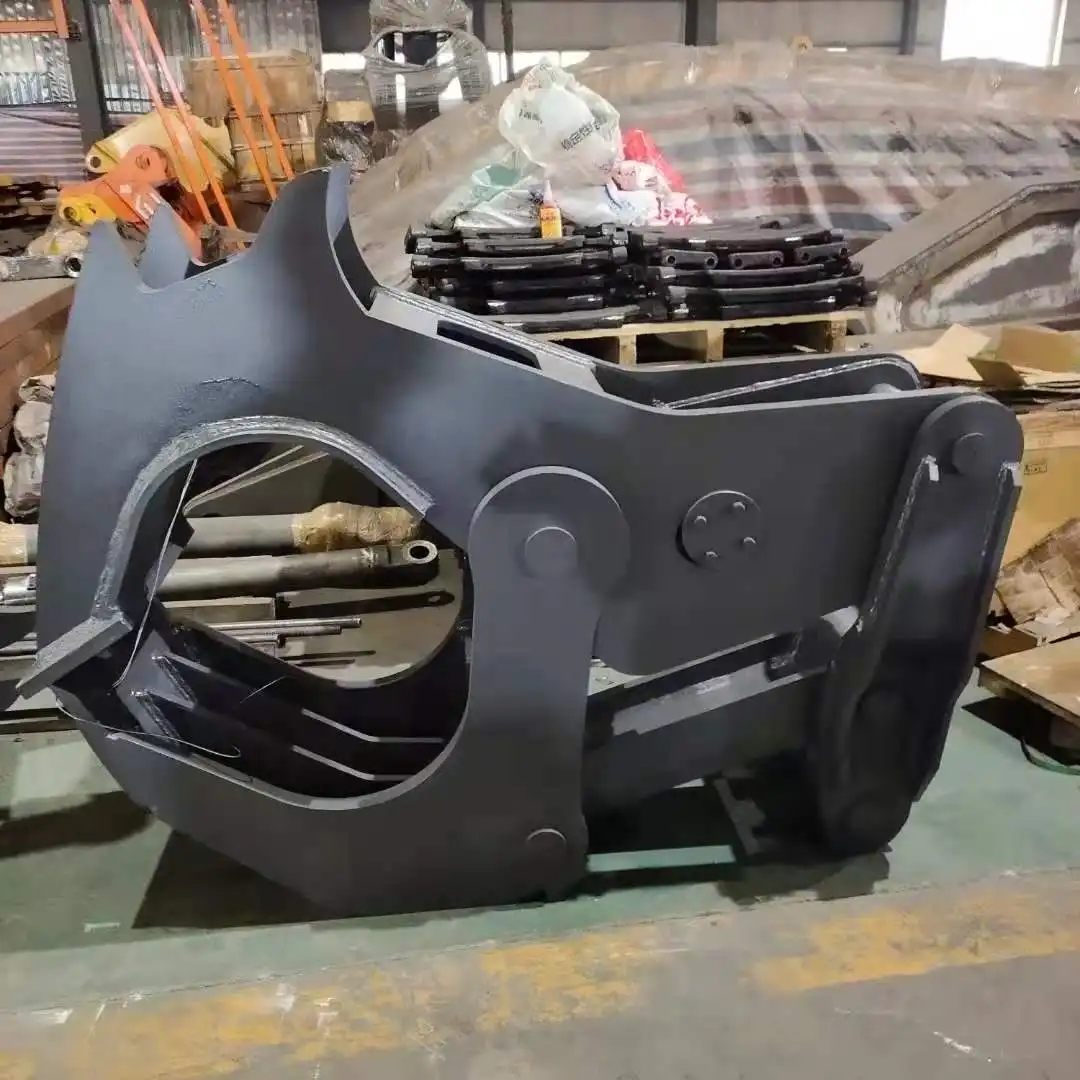
The excavator wood splitter from Tiannuo Machinery is a versatile and powerful tool designed primarily for sawing wood used in the manufacturing of doors, windows, furniture, and wooden molds. With its impressive cutting speed of 30-60 m/s, this machine ensures efficient and precise sawing operations.
Key components of the Tiannuo excavator wood splitter include:
- The body: Serves as the main structure, providing stability and support
- The saw wheel: Drives the cutting process with high efficiency
- Lifting and tilting device: Allows for adjustments to the saw wheel position, enabling various types of cuts
- Saw card device: Guides the saw blade, prevents vibration during high-speed movement, and ensures cut accuracy and quality
If you're in the market for a reliable and efficient excavator wood splitter, Tiannuo Machinery offers top-quality solutions tailored to your needs. For more information or to discuss your specific requirements, please don't hesitate to contact our team:
- Manager: arm@stnd-machinery.com
- Team member: rich@stnd-machinery.com
- Team member: tn@stnd-machinery.com
Choose Tiannuo Machinery for your excavator wood splitter needs and experience the difference in quality, efficiency, and customer service.
References:
- Forest Products Laboratory. (2010). Wood handbook: Wood as an engineering material. USDA Forest Service.
- Hartler, N. (1986). Wood Quality and Chip Preparation in Mechanical Pulping. Paperi ja Puu, 68(5), 362-368.
- Zobel, B. J., & Van Buijtenen, J. P. (2012). Wood variation: its causes and control. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Simpson, W. T. (1999). Drying and control of moisture content and dimensional changes. Wood handbook: Wood as an engineering material, 12-1.
- Spinelli, R., Nati, C., & Magagnotti, N. (2009). Using modified forwarders to harvest short rotation poplar plantations. Biomass and Bioenergy, 33(5), 817-821.
- Miyata, E. S. (1980). Determining fixed and operating costs of logging equipment. General Technical Report NC-55. St. Paul, MN: US Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, North Central Forest Experiment Station.