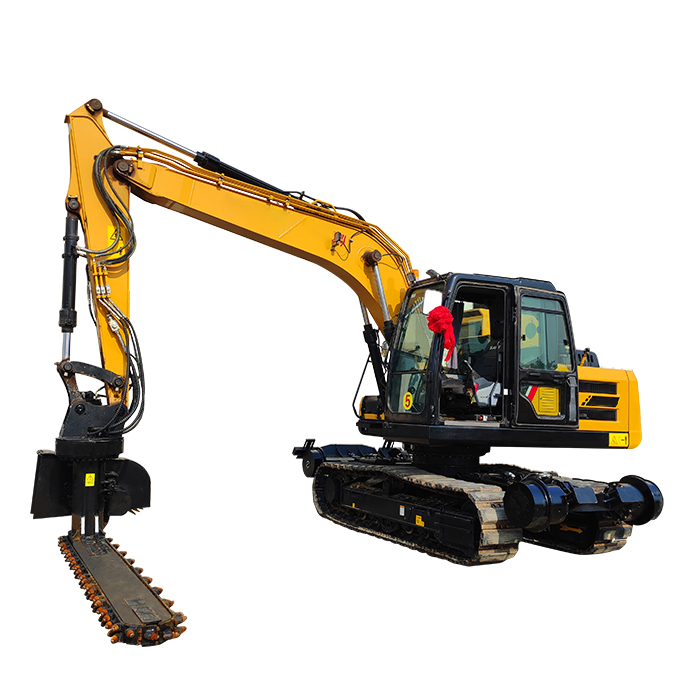
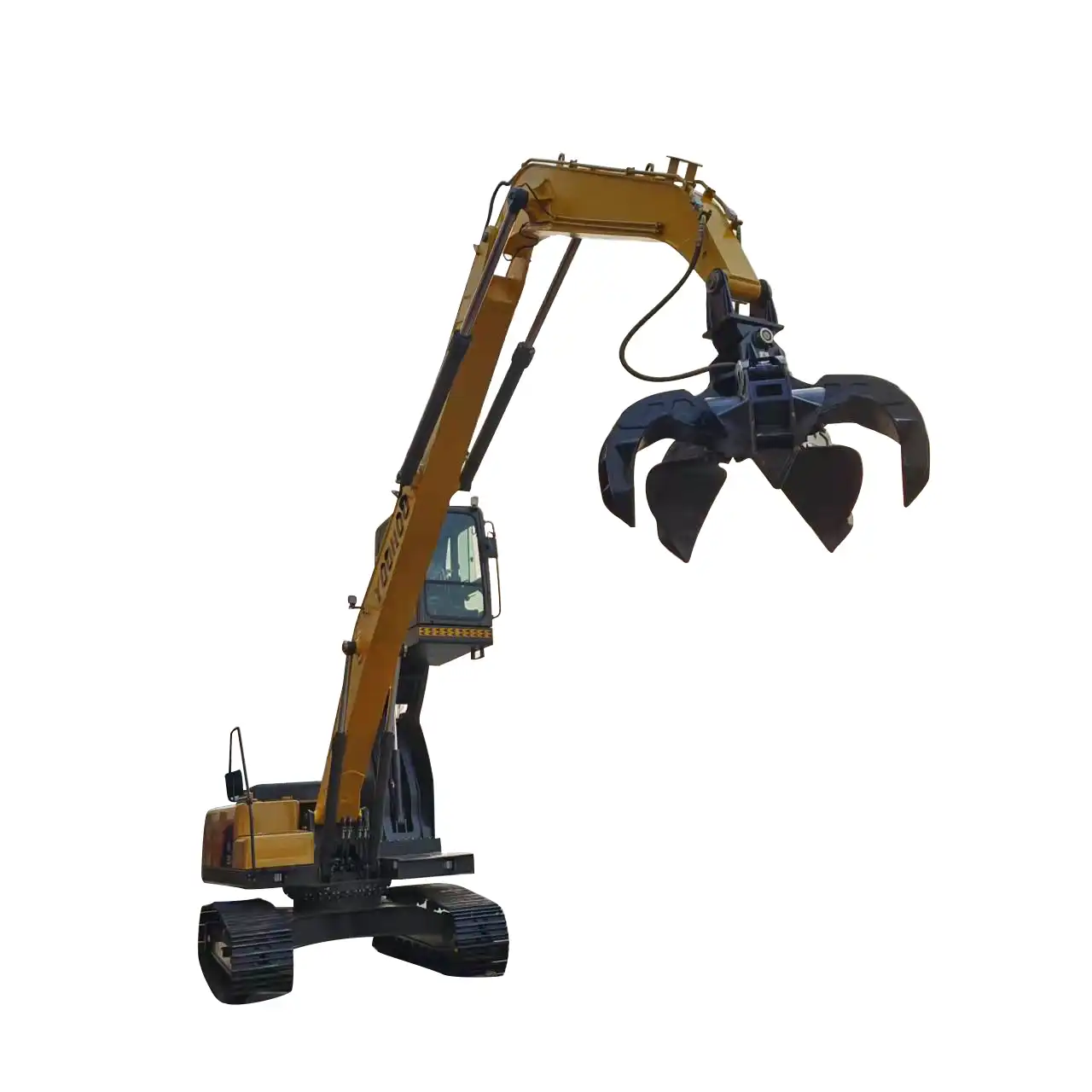
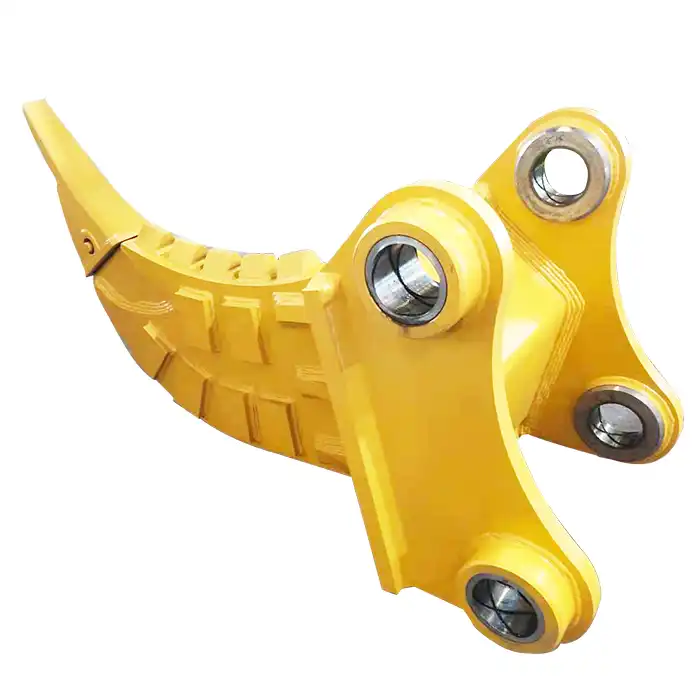
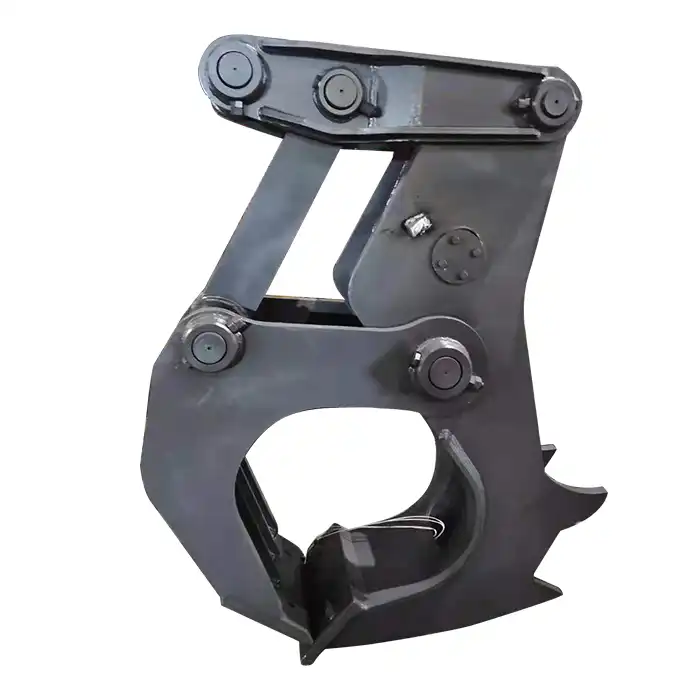
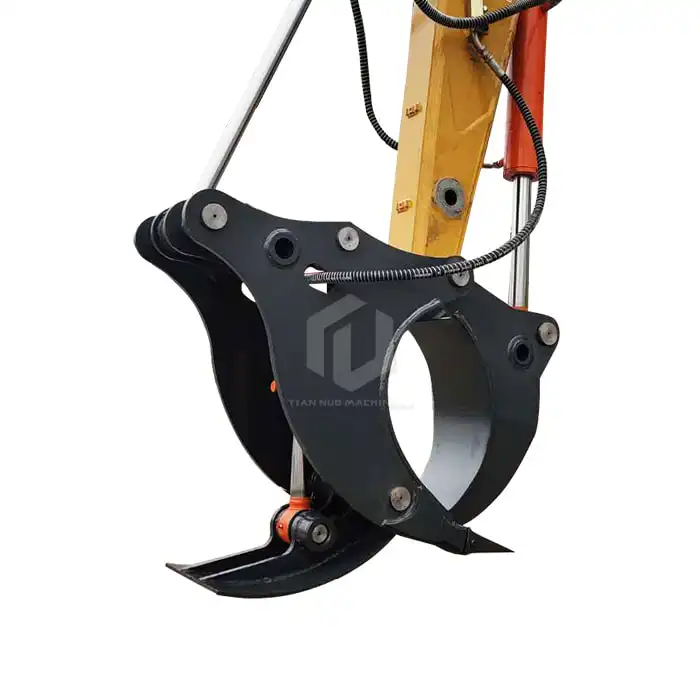
What materials are used to construct the excavator grab arm?
Excavator grab arms are crucial components in construction and material handling operations. These versatile attachments enhance the functionality of excavators, allowing them to efficiently grasp, move, and manipulate various materials. To ensure optimal performance and durability, manufacturers carefully select specific materials for different parts of the excavator grab arm. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the primary materials used in constructing these essential tools, focusing on high-strength alloy plates for arms, 40Cr steel for pin shafts, and brass bushings for the arm base.

High-Strength Alloy Plates For Arms
The arms of an excavator grab are subjected to immense stress and strain during operation. To withstand these forces and maintain structural integrity, manufacturers opt for high-strength alloy plates. These plates are typically made from advanced steel alloys that offer an excellent combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
One commonly used material for excavator grab arms is high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel. HSLA steel contains small amounts of alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium, which enhance its mechanical properties. These alloys provide superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional carbon steels, allowing for lighter yet more robust arm constructions.
Another popular choice for excavator grab arms is manganese steel, also known as Hadfield steel. This material is renowned for its exceptional work-hardening ability, meaning it becomes stronger and harder when subjected to impact or high pressure. This unique property makes manganese steel ideal for applications involving heavy wear and abrasion, such as in excavator grab arms used for handling rough materials like rocks or demolition debris.
Some manufacturers also utilize advanced composite materials in combination with high-strength alloys to further optimize their performance. These composites, often reinforced with carbon or glass fibers, can provide additional strength and reduced weight, potentially improving the overall efficiency and capacity of the excavator.
40Cr Steel For Pin Shafts
The pin shafts in an excavator grab arm play a critical role in facilitating movement and bearing loads. These components require a material that offers high strength, excellent wear resistance, and good machinability. 40Cr steel, also known as SAE 5140 or DIN 1.7035, is a popular choice for this application.
40Cr steel is a medium carbon chromium alloy steel that provides a balanced combination of strength and toughness. The addition of chromium enhances the steel's hardenability, allowing it to achieve high strength levels through heat treatment processes. This material's properties make it well-suited for heavily loaded parts like pin shafts in excavator grab arms.
The chemical composition of 40Cr steel typically includes:
- Carbon: 0.38-0.45%
- Chromium: 0.90-1.20%
- Manganese: 0.60-0.90%
- Silicon: 0.15-0.35%
This composition results in a material with a tensile strength ranging from 900 to 1100 MPa after heat treatment, providing the necessary strength to withstand the high stresses experienced by pin shafts during excavator grab arm operation.
Manufacturers often apply additional surface treatments to 40Cr steel pin shafts to further enhance their performance. These treatments may include carburizing, nitriding, or induction hardening, which increase the surface hardness and wear resistance while maintaining a tough core. This combination of properties ensures that the pin shafts can withstand the dynamic loads and potential impacts encountered during excavation and material handling tasks.
Brass Bushings for Arm Base
Bushings play a crucial role in the smooth operation of an excavator grab arm by reducing friction between moving parts and providing a wear surface that can be easily replaced. Brass is a popular material choice for these bushings, particularly in the arm base area, due to its unique properties and performance characteristics.
Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, with the exact composition varying depending on the specific grade used. For excavator grab arm bushings, manufacturers often choose grades with higher zinc content, such as C84400 (also known as 660 bearing bronze) or C93200 (also called SAE 660). These grades offer an excellent balance of strength, wear resistance, and self-lubricating properties.
The advantages of using brass bushings in excavator grab arms include:
- Low friction: Brass has naturally low friction properties, which helps reduce wear on mating parts and minimizes the need for frequent lubrication.
- Good thermal conductivity: Brass efficiently dissipates heat generated by friction, helping to prevent overheating and premature wear of components.
- Corrosion resistance: Brass exhibits good resistance to corrosion, which is beneficial in the often harsh operating environments of excavators.
- Conformability: Brass can slightly deform under load, allowing it to distribute forces more evenly and potentially accommodate minor misalignments.
- Embeddability: The soft nature of brass allows it to embed small particles of debris, preventing them from causing damage to the mating surfaces.
In some cases, manufacturers may opt for composite bushings that incorporate brass with other materials, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or graphite. These composite bushings can offer even lower friction coefficients and improved wear resistance, potentially extending the service life of the excavator grab arm components.
The selection of brass bushings for the arm base of excavator grab arms is not arbitrary. Engineers carefully consider factors such as load capacity, operating speed, and environmental conditions to determine the most suitable brass alloy and bushing design. This attention to detail ensures that the bushings can withstand the demanding conditions of excavator operation while providing smooth and reliable performance.
Excavator Grab Arm Manufacturer
Are you looking for a reliable and efficient excavator grab arm to boost your construction or logistics operations? Look no further than Tiannuo Machinery. Our excavator grab arm is meticulously crafted with high-strength alloy plates for the arms, cold-drawn seamless pipes for iron pipes, 40Cr steel for pin shafts, and brass bushings for the arm base. Our manufacturing process includes beveling welding to prevent deformation, shot blasting to eliminate internal stress, and post-welding treatment with grinding, painting, quality inspection, and warehousing. This ensures that our product is built for heavy-duty performance and will improve material handling efficiency. Don't miss out on this opportunity to enhance your operations. Contact our manager at arm@stnd-machinery.com or reach out to our team members at rich@stnd-machinery.com and tn@stnd-machinery.com for more information and to place your order today.
References:
- Llewellyn, D. T., & Hudd, R. C. (1998). Steels: metallurgy and applications. Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Subramanyam, D. K., Swansiger, A. E., & Avery, H. S. (1990). Austenitic manganese steels. ASM Handbook, 1, 822-840.
- Chawla, K. K. (2012). Composite materials: science and engineering. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Davis, J. R. (Ed.). (1996). ASM specialty handbook: carbon and alloy steels. ASM international.
- Bhadeshia, H., & Honeycombe, R. (2017). Steels: microstructure and properties. Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Krauss, G. (2015). Steels: processing, structure, and performance. ASM international.