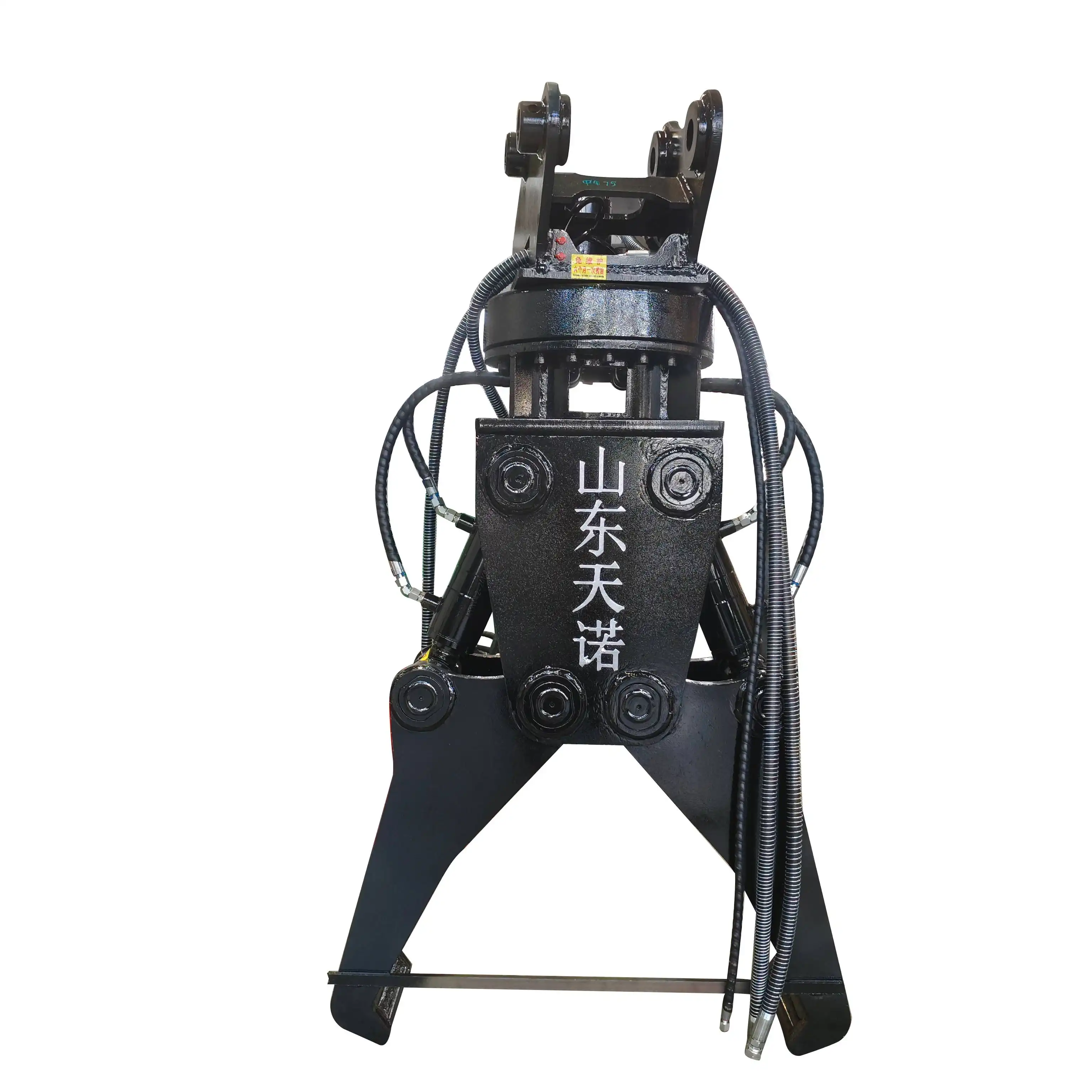
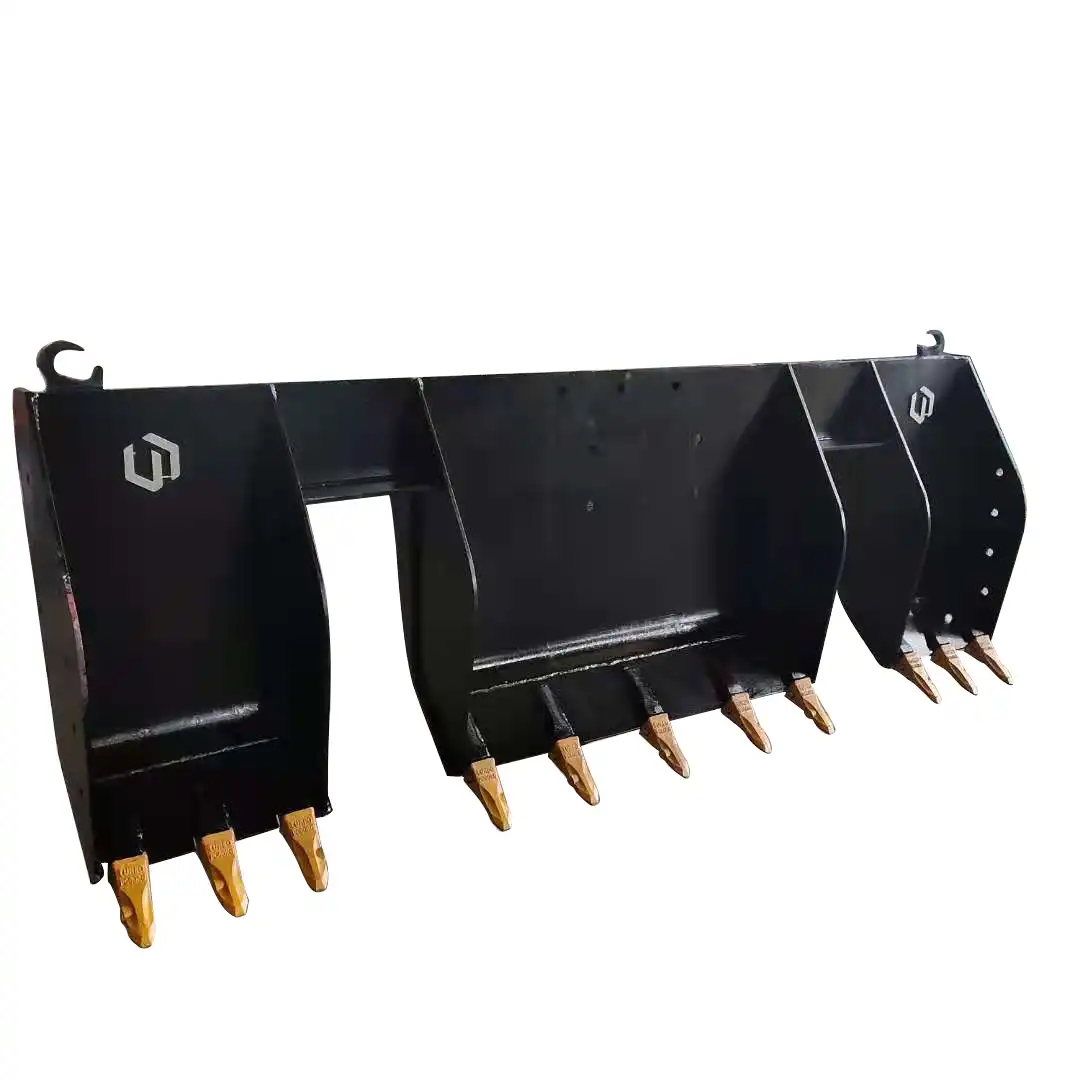
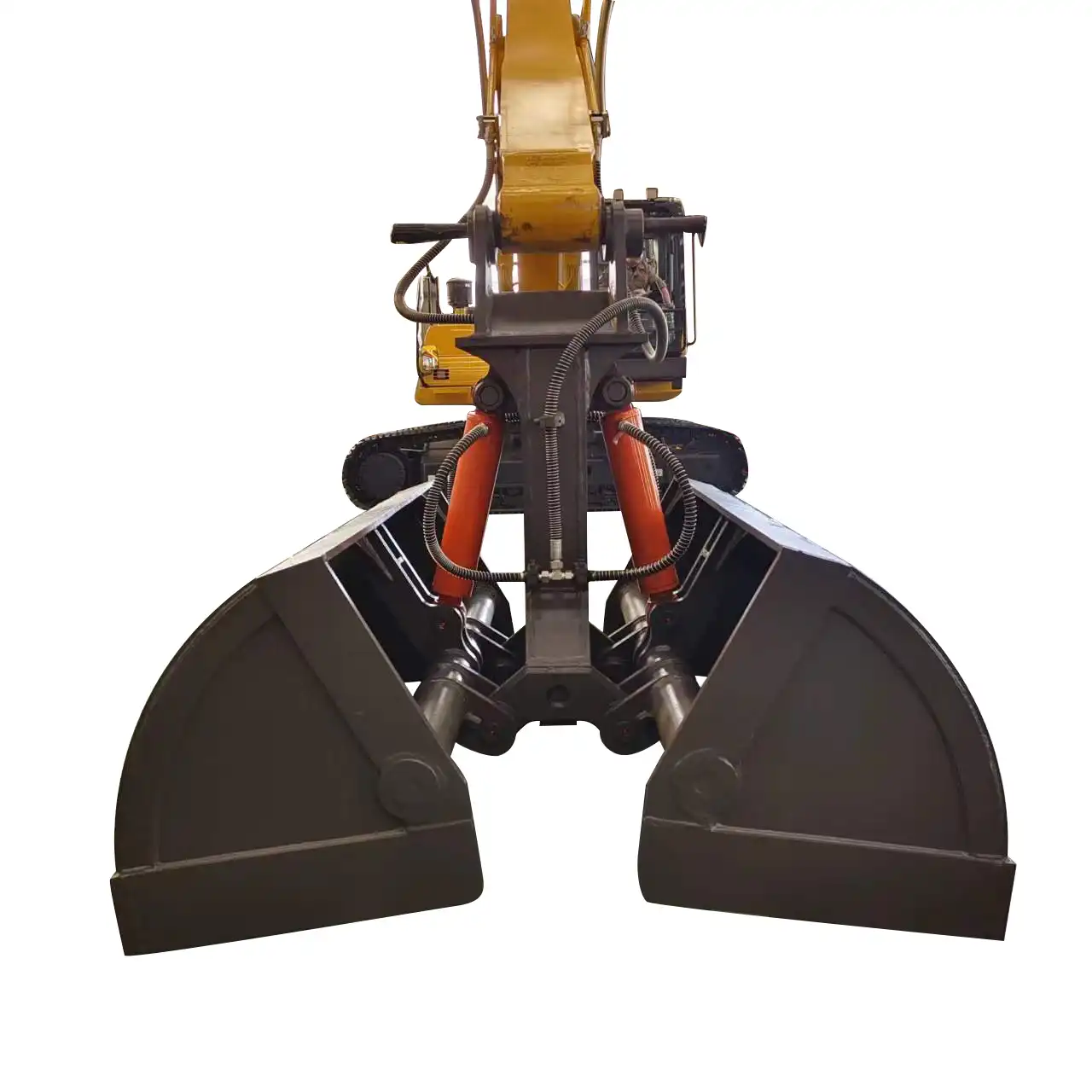
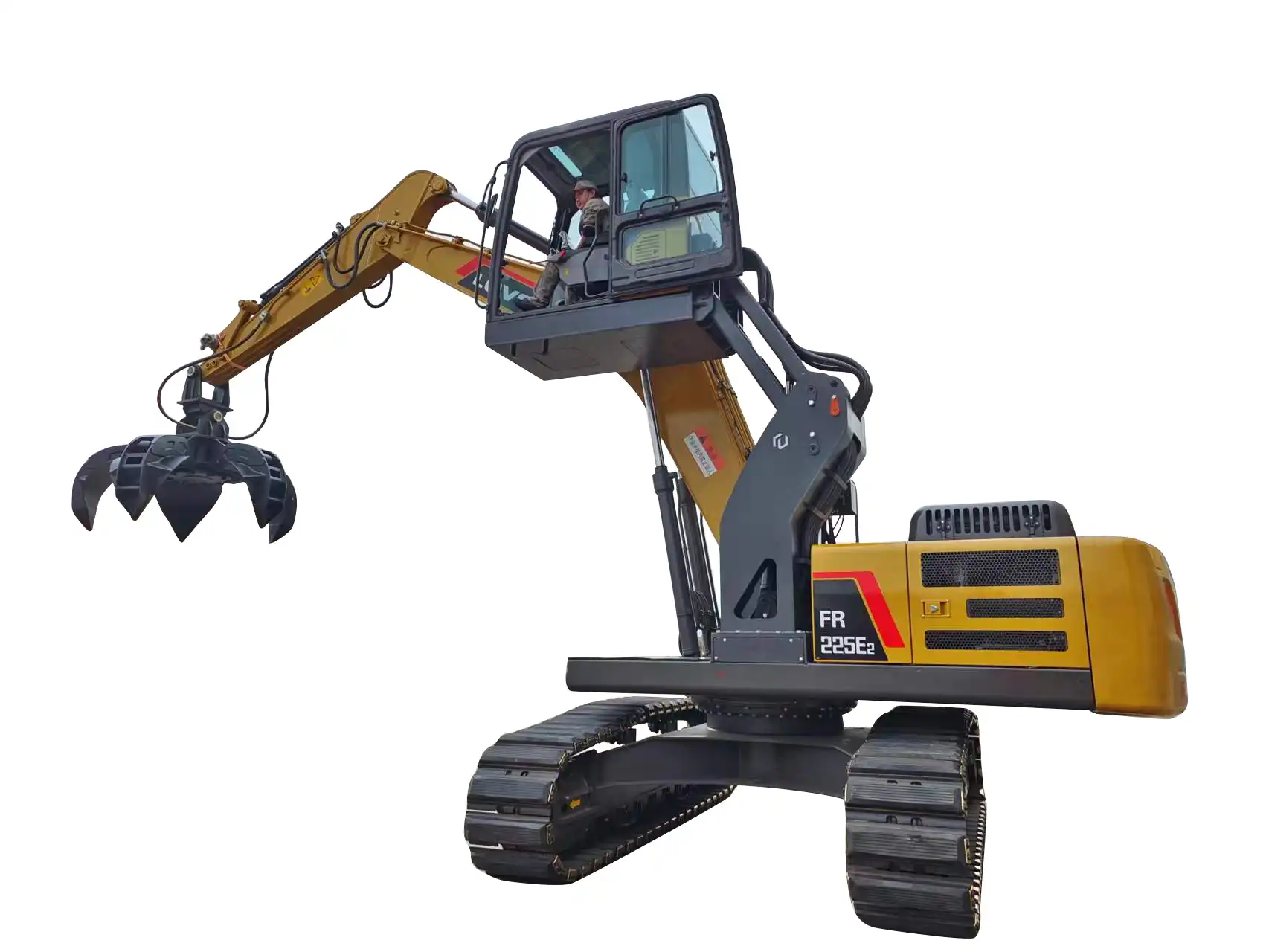
What do excavator grippers do?
Excavator grippers transform conventional digging equipment into multipurpose tools capable of grasping, sorting, lifting, and manipulating various materials with precision and control. Its primary function is to provide a mechanical means of securely holding and moving objects that would otherwise be difficult to manage with standard buckets alone. From construction debris and scrap metal to logs and concrete blocks, these attachments enable operators to handle diverse materials efficiently across multiple industries and applications.
Operating through hydraulic systems that connect directly to the excavator's existing infrastructure, these attachments utilize opposing jaws or tines that close around materials with calculated pressure.
Function
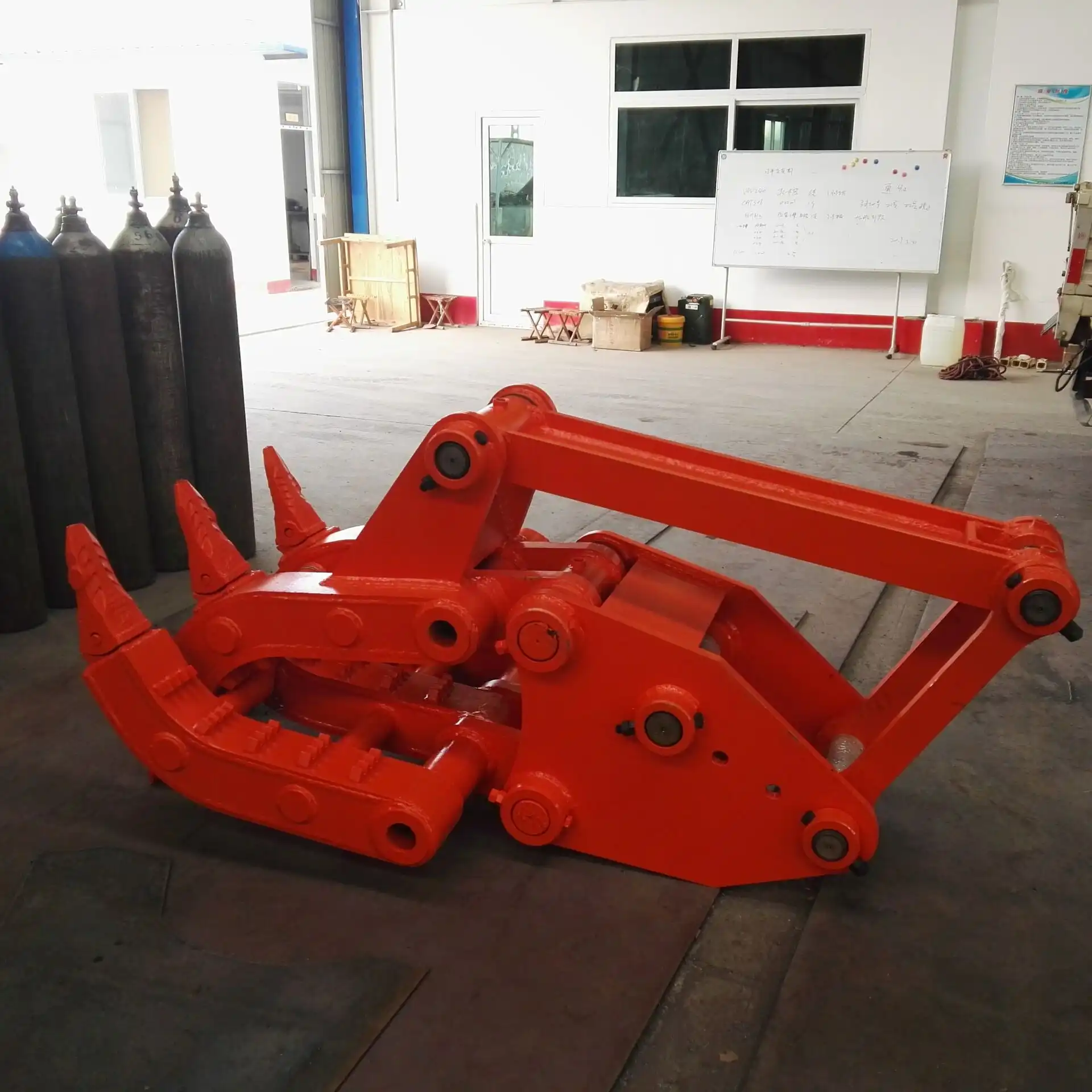

Operational Mechanics
The operational mechanics of excavator grippers involve sophisticated hydraulic systems working in coordination with mechanical components to deliver powerful gripping capabilities. At the core of their functionality lies a hydraulic cylinder system that converts fluid pressure into mechanical force, allowing the gripper jaws to open and close with precision and strength. This hydraulic actuation provides operators with fine control over gripping pressure, enabling them to handle both robust materials requiring significant force and delicate items demanding gentler manipulation.
Most gripper designs incorporate pivot points that create mechanical advantage, multiplying the hydraulic force to generate substantial gripping power. This mechanical efficiency allows relatively compact cylinders to produce impressive holding strength at the jaw interface. The articulation mechanisms vary across different models, with some utilizing direct cylinder attachment to moving jaws while others employ more complex linkage systems to optimize jaw movement patterns or force distribution.
Grip Control Systems
Modern excavator gripper attachments employ various control systems that enable operators to achieve precise material handling capabilities. These systems range from basic hydraulic controls to sophisticated electronic interfaces that provide enhanced functionality and feedback.
The most fundamental grip control systems utilize direct hydraulic actuation, where operator inputs through joysticks or pedals translate directly to hydraulic pressure applied to gripper cylinders. More advanced systems incorporate proportional control valves that allow variable pressure application, giving operators the ability to adjust gripping force based on material characteristics and handling requirements. This proportional control proves invaluable when handling materials with varying fragility or structural integrity.
Power and Force Distribution
The effectiveness of excavator grippers largely depends on their power generation capabilities and how efficiently they distribute force across their gripping surfaces. Understanding these aspects is crucial for selecting the appropriate gripper for specific applications and materials.
Hydraulic power requirements for excavator grippers vary significantly based on design and intended use, typically ranging from 1,500 to 5,000 PSI depending on model specifications. The excavator's hydraulic system must provide sufficient flow rates, usually between 20 to 60 gallons per minute, to ensure optimal gripper performance. Inadequate hydraulic capacity can result in sluggish operation, reduced gripping force, or overheating of the hydraulic system.
Force distribution across gripper jaws significantly impacts material handling effectiveness. Well-designed grippers feature jaw geometries that distribute pressure evenly across contact surfaces, preventing localized stress points that could damage materials or cause slippage. Specialized jaw designs incorporate serrations, textured surfaces, or interdigitating tines that enhance grip security without requiring excessive clamping pressure.
Load capacity ratings for excavator grippers typically range from 2 to 20 tons, depending on size and construction. These ratings consider not only the gripper's structural integrity but also the stress limitations of mounting points and the excavator's stability envelope. Operating beyond rated capacities compromises safety and accelerates component wear, potentially leading to premature failure or hazardous situations.
Uses
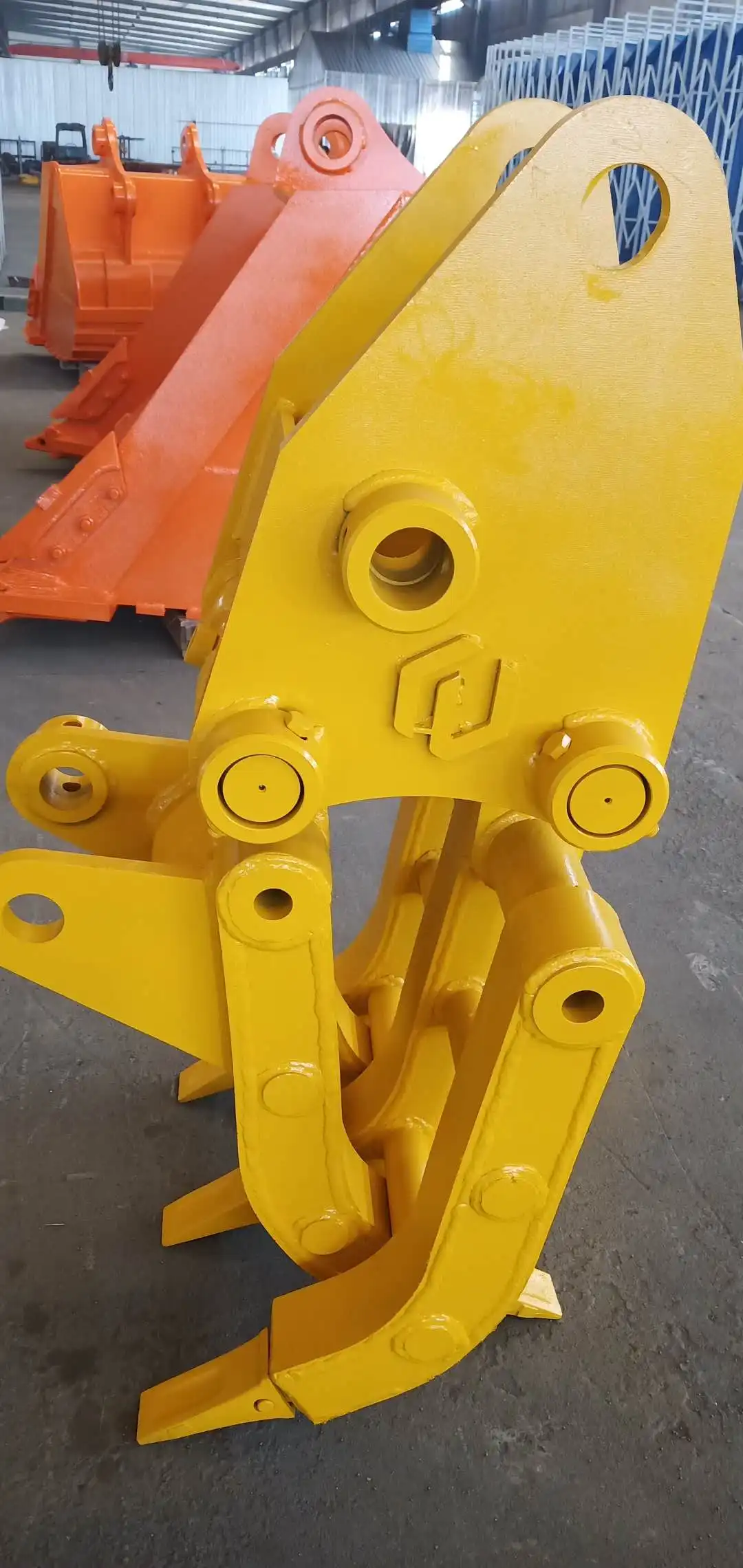

Construction and Demolition Applications
In construction and demolition environments, excavator grippers serve as multifunctional tools that streamline operations and enhance productivity across numerous tasks. Their versatility proves invaluable for projects requiring precise material handling and sorting capabilities.
During demolition projects, grippers excel at controlled structural dismantling, allowing operators to grasp and remove specific building elements with precision. This selective demolition capability proves particularly valuable in urban environments where noise reduction and debris containment are paramount concerns. The ability to grip and hold materials during cutting operations increases safety by preventing unexpected movement or falls of severed structural components.
Concrete recycling operations benefit immensely from excavator grippers, which efficiently separate reinforcing steel from concrete debris. This material segregation accelerates processing times and improves the quality of recycled aggregate. Grippers equipped with specialized crushing jaws can perform preliminary size reduction directly at the demolition site, reducing transportation costs and processing requirements at recycling facilities.
Waste Management and Recycling
The waste management and recycling sectors utilize excavator grippers extensively for handling, sorting, and processing various materials within treatment facilities and collection sites. These attachments provide the versatility needed to manage the diverse material streams encountered in modern waste processing operations.
In material recovery facilities, excavator grippers sort and separate different waste types with efficiency that surpasses manual methods. Their ability to selectively grasp specific items from mixed waste piles enables operators to extract high-value recyclables or contaminants that require special handling. This selective capability improves recycling rates and reduces contamination in processed material streams.
Scrap metal recycling operations rely heavily on grippers to handle and process various metal types and forms. The robust gripping capability allows for secure manipulation of irregularly shaped metal objects, while specialized jaw designs prevent damage to valuable materials. Grippers facilitate the feeding of shredders, balers, and other processing equipment, maintaining continuous operation and maximizing throughput.
Composting facilities employ grippers for turning and aerating compost windrows, mixing different organic materials, and loading finished compost for distribution. The open tine design common in these applications allows excess moisture to drain while maintaining a secure grip on organic materials. This drainage capability helps maintain optimal moisture content in compost piles while preventing equipment from becoming waterlogged during manipulation.
Forestry and Material Handling
The forestry industry and various material handling operations benefit significantly from the specialized capabilities that excavator grippers provide. These attachments enable efficient processing and transportation of logs, bulk materials, and other challenging items that require secure handling.
Timber harvesting operations utilize excavator grippers for gathering felled trees, delimbing trunks, and loading logs onto transportation vehicles. Specialized forestry grippers feature tine designs that penetrate between logs in piles, allowing selective extraction without disturbing surrounding materials. This selective capability improves sorting efficiency and reduces damage to valuable timber products during handling.
Log yard management relies on grippers for stacking, sorting, and loading activities that maintain organized inventory and efficient space utilization. The rotational capabilities of modern grippers allow operators to precisely align logs during stacking, creating stable piles that maximize storage capacity while maintaining safe work environments. Grippers equipped with measuring systems can assist in log scaling and quality assessment during handling phases.
Bulk material handling across various industries benefits from excavator grippers designed for specific material characteristics. Port operations use grippers for handling bulk commodities like coal, grain, or minerals, often employing specialized jaw designs that prevent material spillage while maintaining high throughput rates. Manufacturing facilities utilize grippers for raw material management, particularly for awkwardly shaped items that conventional buckets cannot effectively manipulate.
Types
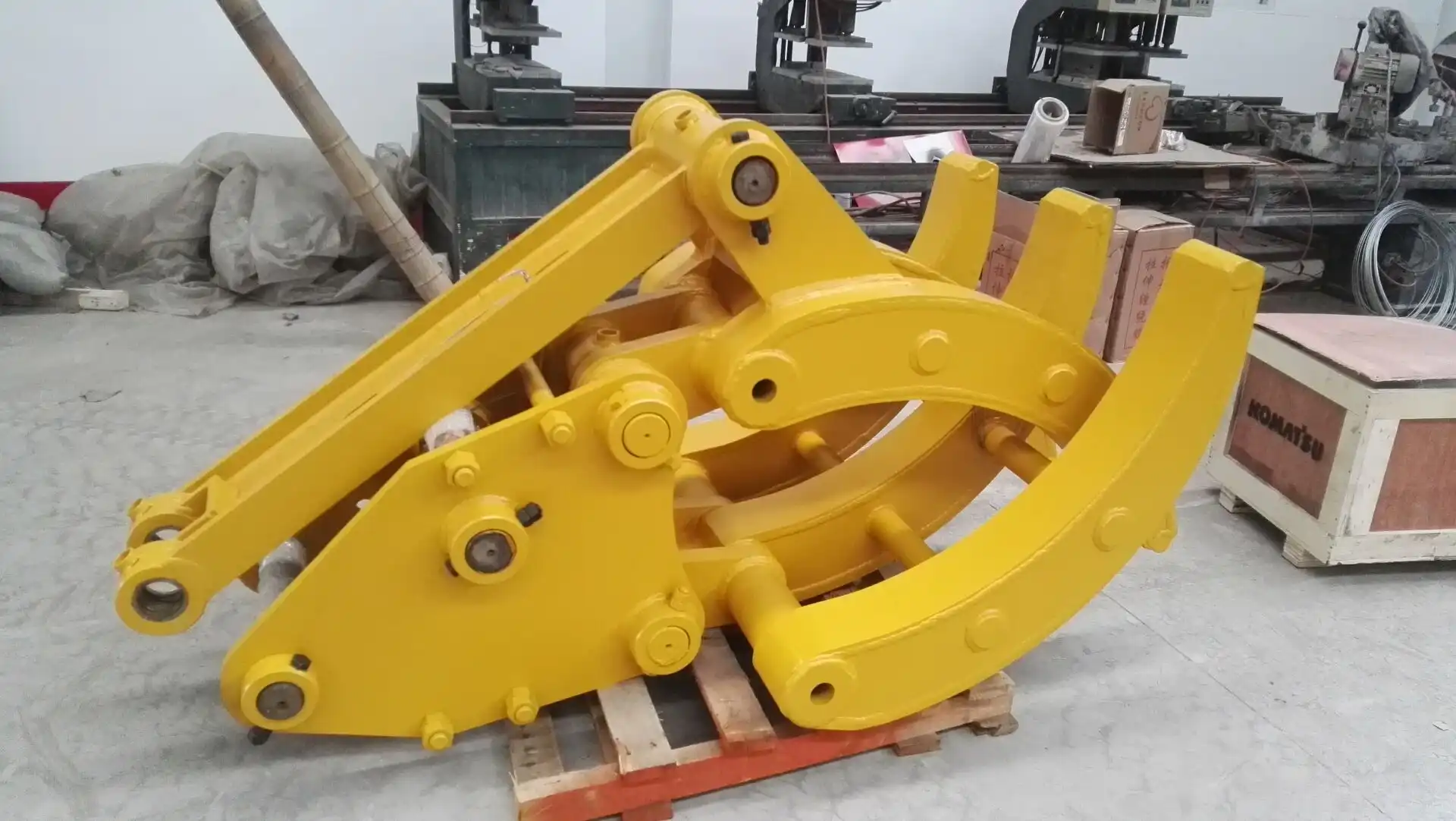

Grapples
Grapple-style attachments represent one of the most versatile and widely used categories of excavator grippers, with various designs optimized for specific applications and materials. These attachments feature multiple tines or fingers that interlock when closed, providing secure containment while allowing debris and smaller materials to fall through the openings.
Orange peel grapples, named for their resemblance to orange segments when open, typically feature four to six curved tines that close toward a central point. This design excels in handling irregular materials like demolition debris, scrap metal, and industrial waste. The curved tine geometry creates a basket-like enclosure when closed, effectively containing loose materials while maintaining visibility for the operator. These grapples often incorporate rotation capabilities, allowing orientation adjustment without repositioning the entire excavator.
Sorting grapples feature parallel tines with consistent spacing throughout their length, optimized for separating mixed materials during recycling and waste management operations. The uniform gaps between tines allow smaller debris to fall through while retaining larger target materials, performing preliminary sorting during the gripping process. Advanced sorting grapples include interchangeable tine sets with different spacing configurations to accommodate various material sizes and types.
Log grapples incorporate heavy-duty tines specifically designed for forestry applications, with robust construction to withstand the substantial weight and irregular shape of timber products. These specialized grapples often feature bypass tine arrangements that allow deeper penetration into log piles for selective extraction. High-capacity hydraulic systems support these grapples to provide the substantial gripping force required for secure timber handling across challenging terrain and operating conditions.
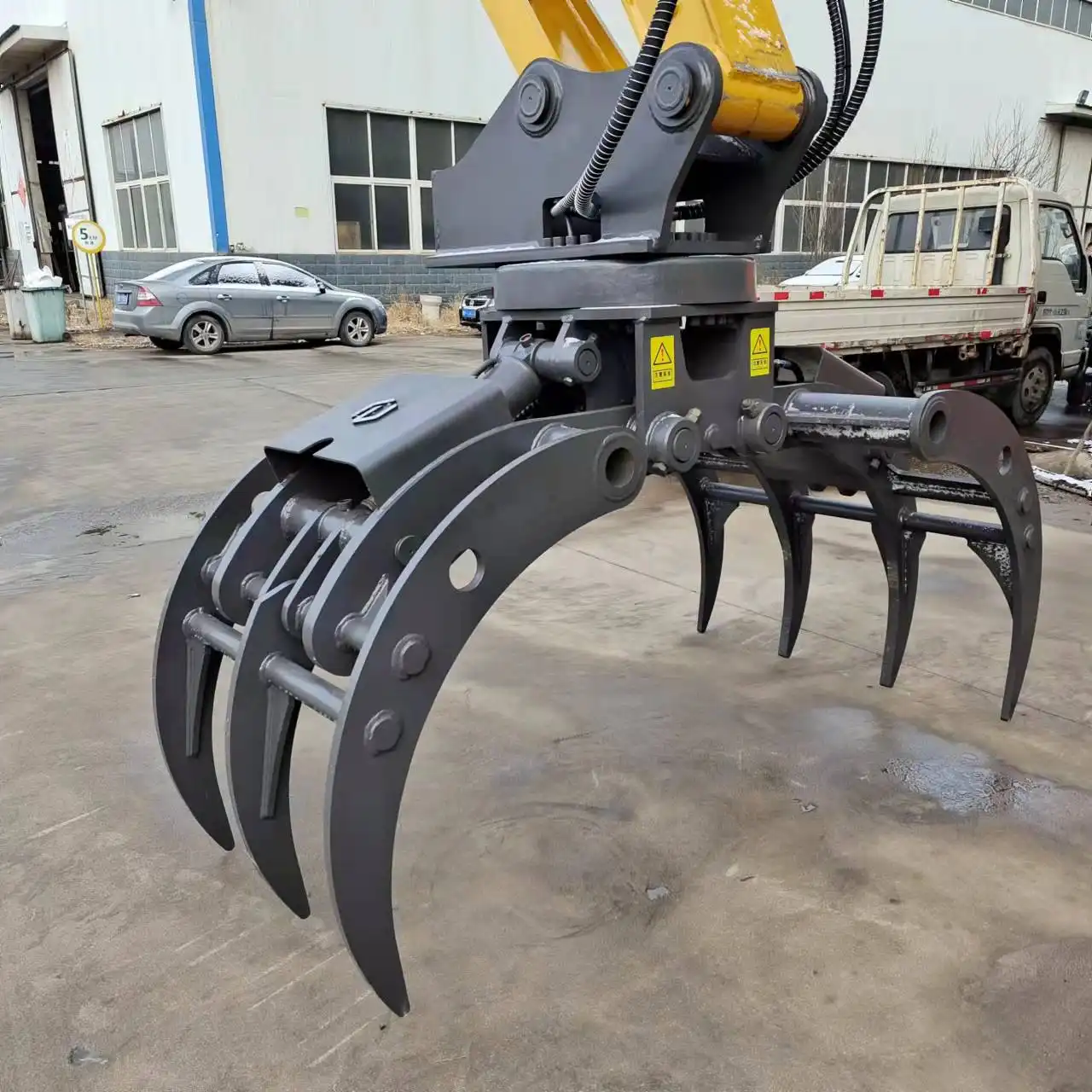
Thumbs
Excavator thumbs represent a fundamental gripper category that transforms conventional excavator buckets into versatile gripping tools through the addition of a single opposing jaw. This straightforward yet effective design creates a thumb-and-finger arrangement when paired with the excavator bucket, enabling secure gripping without requiring complete attachment replacement.
Progressive link thumbs feature sophisticated multi-joint linkage systems that maintain parallel alignment between the thumb and bucket throughout the gripping range. This advanced design ensures consistent pressure distribution across irregularly shaped materials, improving grip security and reducing material damage. The parallel action proves particularly valuable when handling fragile materials or precisely stacking items with uniform pressure requirements.
Hydraulic thumbs incorporate dedicated hydraulic cylinders that provide independent operation and precise control over thumb position and pressure. This hydraulic actuation enables operators to adjust gripping force based on material characteristics, applying sufficient pressure for security without causing damage. Modern hydraulic thumbs feature integrated pressure relief valves that prevent overloading and proportional control systems that allow fine adjustments to gripping pressure during operation.
FAQ

1. What hydraulic requirements do excavator grippers have?
Excavator grippers typically require hydraulic systems capable of delivering 1,500-5,000 PSI with flow rates between 20-60 gallons per minute, depending on gripper size and application.
2 . How do I choose the right excavator gripper for my application?
Selecting the appropriate gripper involves analyzing several critical factors including material types being handled, required grip strength, excavator compatibility, and operational environment. Consider the primary materials you'll be gripping—whether logs, concrete, scrap metal, or mixed debris—as each requires specific jaw designs and configurations.
3 . What maintenance do excavator grippers require?
Regular maintenance includes daily visual inspections of hydraulic components, greasing of pivot points every 8-10 operating hours, and thorough cleaning after each shift to remove debris from moving parts. Hydraulic system maintenance involves checking hoses for wear or damage, inspecting fittings for leaks, and monitoring fluid levels and quality. Structural components require weekly inspection for cracks, deformation, or excessive wear, particularly at high-stress points like jaw tips and pivot bushings. Replace worn cutting edges or wear plates according to manufacturer recommendations, typically when wear exceeds 1/4 inch fromthe original dimensions. Follow manufacturer-specified torque checks on all bolted connections at recommended intervals, usually every 40-50 operating hours.
4. What safety considerations are important when using excavator grippers?
Safety considerations for excavator gripper operations include maintaining appropriate working distances—typically 1.5 times the machine's reach—from other workers and equipment. Operators must receive specific training on gripper operation, including load limitations, stability considerations, and emergency procedures. Regular inspection of safety systems, including pressure relief valves, load monitoring devices, and emergency shutoffs, is essential for preventing accidents.
Excavator Gripper Supplier

For more information about Tiannuo's comprehensive range of excavator gripper attachments designed for diverse applications, please contact our technical team at arm@stnd-machinery.com, rich@stnd-machinery.com, or tn@stnd-machinery.com. Our specialists can provide detailed guidance on selecting the optimal gripper configuration for your specific requirements and operational environment.
References

Heavy Equipment Engineering Journal: Hydraulic Attachment Systems and Applications, Volume 28, 2023
Construction Materials Handling: Innovations in Excavator Attachment Design, 3rd Edition
International Journal of Forestry Equipment and Techniques, Special Issue on Material Handling
Handbook of Demolition Engineering: Equipment Selection and Application Strategies
Waste Management Technology Review: Equipment Evolution and Processing Efficiency, Volume 14
Railway Maintenance Equipment Standards and Practices, 2023 Technical Compendium
About Author: Arm
Arm is a leading expert in the field of specialized construction and railway maintenance equipment, working at Tiannuo Company.