Analysis of load capacity and applicable scope of rail track trolley
Rail track trolleys are essential components in various industries, providing efficient transportation of heavy loads along railway tracks. Understanding their load capacity, applicable scope, and performance limits is crucial for optimal utilization and safety. This comprehensive analysis delves into the factors determining load capacity, methods for calculating optimal load distribution, and the performance boundaries of standard rail trolleys under heavy loads.

What Factors Determine the Load Capacity of a Rail Track Trolley?
The load capacity of a rail track trolley is influenced by several key factors, each playing a vital role in determining its overall performance and safety. These factors include:
1. Structural Design: The trolley's frame and components are fundamental in determining its load-bearing capacity. The materials used, such as high-strength steel like Q355, contribute significantly to the trolley's ability to withstand heavy loads. The design of load-bearing elements, including the frame, axles, and wheels, must be engineered to distribute weight evenly and resist deformation under stress.
2. Wheel Specifications: The wheels are critical components that directly impact load capacity. Factors such as wheel diameter, width, and material composition (e.g., 40Cr steel) affect the trolley's ability to support and distribute weight. Larger wheels generally offer better load distribution and reduced rolling resistance, while the material's durability ensures longevity under heavy loads.
3. Track Gauge: The compatibility between the trolley's wheel spacing and the railway track gauge is crucial. Standard track gauges like 1000 mm, 1067 mm, 1435 mm, and 1520 mm require specific trolley configurations to ensure stability and proper weight distribution. A mismatch can lead to reduced load capacity and increased risk of derailment.
4. Axle Count and Configuration: The number of axles and their arrangement significantly influence a trolley's load capacity. More axles generally allow for higher load capacities by distributing weight over a larger area. However, this must be balanced with considerations of maneuverability and track compatibility.
5. Suspension System: While not all rail track trolleys have suspension systems, those that do can offer improved load capacity and performance. Suspension helps absorb shocks and vibrations, reducing stress on the trolley's structure and allowing for smoother operation under varying load conditions.
6. Safety Factors: Engineers typically incorporate safety factors into load capacity calculations. These factors account for unexpected stresses, material imperfections, and other variables that could affect performance. A common practice is to design the trolley to safely handle loads greater than its stated capacity.
7. Regulatory Standards: Industry and government regulations often dictate minimum safety standards and load capacities for rail track trolleys. Compliance with these standards is essential for legal operation and ensures that the trolley meets recognized safety benchmarks.
Understanding these factors is crucial for both manufacturers and users of rail track trolleys. It allows for the design and selection of trolleys that are optimally suited for specific applications, ensuring safe and efficient operations in various industrial settings.
How to Calculate the Optimal Load Distribution for Rail Track Trolleys
Calculating the optimal load distribution for rail track trolleys is a critical process that ensures safe and efficient operation. This process involves several steps and considerations:
1. Determine Total Load Weight: The first step is to accurately measure the total weight of the load to be transported. This includes not only the primary cargo but also any additional equipment or materials that will be placed on the trolley.
2. Assess Load Dimensions: The size and shape of the load are crucial factors. Measure the length, width, and height of the cargo to ensure it fits within the trolley's dimensions and doesn't exceed any clearance limits along the intended route.
3. Identify the Center of Gravity: Locate the load's center of gravity. This is essential for maintaining stability during transport. Ideally, the center of gravity should be as low as possible and centered over the trolley's axles.
4. Calculate Axle Loads: Distribute the total load weight across the trolley's axles. This calculation should ensure that no single axle is overloaded. The formula for axle load is:
Axle Load = (Total Load Weight × Distance from opposite axle) ÷ Wheelbase
This calculation should be performed for each axle to ensure balanced distribution.
5. Consider Dynamic Forces: Account for dynamic forces that occur during movement, such as acceleration, deceleration, and cornering. These forces can temporarily increase the effective load on certain parts of the trolley. A general rule is to add a 10-15% safety margin to static load calculations to account for these dynamic forces.
6. Evaluate Track Conditions: The condition and grade of the track can affect load distribution. Uphill or downhill grades will shift the effective center of gravity and change the load distribution. Calculate the additional forces induced by any significant grade changes along the route.
7. Use Load Distribution Software: For complex loads or critical applications, specialized software can provide more accurate load distribution calculations. These tools can model various scenarios and help optimize load placement.
8. Perform Physical Tests: After theoretical calculations, it's advisable to perform physical load tests. This involves gradually increasing the load on the trolley and monitoring its performance, checking for any signs of stress or instability.
9. Implement Safety Margins: Always include a safety margin in your calculations. This typically involves limiting the actual load to 80-90% of the calculated maximum capacity to account for unforeseen circumstances or variations in load dynamics.
10. Document and Communicate: Once the optimal load distribution is determined, clearly document and communicate this information to all relevant personnel. This should include maximum weight limits, load placement guidelines, and any specific handling instructions.
By following these steps, operators can ensure that rail track trolleys are loaded safely and efficiently, maximizing their performance while minimizing the risk of accidents or equipment damage.
What are the Performance Limits of Standard Rail Track Trolleys Under Heavy Loads?
Understanding the performance limits of standard rail track trolleys under heavy loads is crucial for safe and efficient operations. These limits are determined by various factors and can vary depending on the specific design and intended use of the trolley. Here's an analysis of the key performance limits:
1. Maximum Load Capacity: The primary limit for any rail track trolley is its maximum load capacity. This is typically specified by the manufacturer and is based on the trolley's structural design, materials, and safety factors. For standard trolleys, this can range from 10 to 30 tons, though specialized designs can handle much higher loads.
2. Speed Limitations: As the load increases, the maximum safe operating speed of the trolley decreases. This is due to increased inertia and the need for longer stopping distances. Standard trolleys under heavy loads may be limited to speeds of 5-10 km/h to ensure safe operation.
3. Acceleration and Deceleration: Heavy loads significantly impact a trolley's ability to accelerate and decelerate. The time and distance required for these operations increase proportionally with the load weight. This affects operational efficiency and must be considered in planning and safety protocols.
4. Turning Radius: The minimum turning radius of a loaded trolley increases with heavier loads. This is due to the increased forces acting on the wheels and track during turns. Operators must be aware of these limitations to prevent derailment or damage to the track.
5. Track Quality Requirements: Heavier loads place greater stress on the tracks. Standard trolleys operating at or near their maximum capacity may require higher quality tracks with greater load-bearing capacity and more frequent maintenance to prevent track damage or failure.
6. Braking Distance: The distance required to bring a heavily loaded trolley to a complete stop increases significantly. This affects safety considerations and operational planning, particularly in areas with limited sightlines or multiple trolleys operating on the same track.
7. Structural Fatigue: Repeated operation at or near maximum load capacity can lead to accelerated wear and fatigue of the trolley's components. This may reduce the overall lifespan of the equipment and require more frequent inspections and maintenance.
8. Stability on Grades: The ability of a trolley to maintain stability on inclined tracks is reduced under heavy loads. Standard trolleys may have strict grade limitations when fully loaded, typically not exceeding 2-3% grades without additional safety measures.
9. Power Requirements: For powered trolleys, the energy required to move heavy loads increases substantially. This can limit the operational range of battery-powered units or require more powerful motors for diesel or electric-powered trolleys.
10. Environmental Factors: External factors such as wind, rain, or ice can further limit the performance of heavily loaded trolleys. These conditions may necessitate load reductions or operational restrictions to maintain safety.
11. Operator Skill Level: The skill and experience of the operator become increasingly critical as loads approach the trolley's limits. Advanced training may be required for safe operation under maximum load conditions.
12. Regulatory Compliance: Performance limits are often dictated not just by physical capabilities but also by regulatory standards. Operators must ensure that their use of rail track trolleys complies with all relevant safety and operational regulations, which may impose additional limits beyond the equipment's physical capabilities.
Understanding these performance limits is essential for anyone operating or managing rail track trolleys. It allows for proper planning, ensures safe operations, and helps in selecting the right equipment for specific tasks. Regular assessment and adherence to these limits can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and extend the operational life of the equipment.
Rail Track Trolley For Sale
Welcome to Tiannuo Machinery, your reliable partner in the field of heavy machinery. Our dedicated team is always ready to assist you. You can reach out to our esteemed manager at arm@stnd-machinery.com for any inquiries or business discussions. Additionally, our professional team members are available at rich@stnd-machinery.com and tn@stnd-machinery.com to provide you with prompt and comprehensive support.
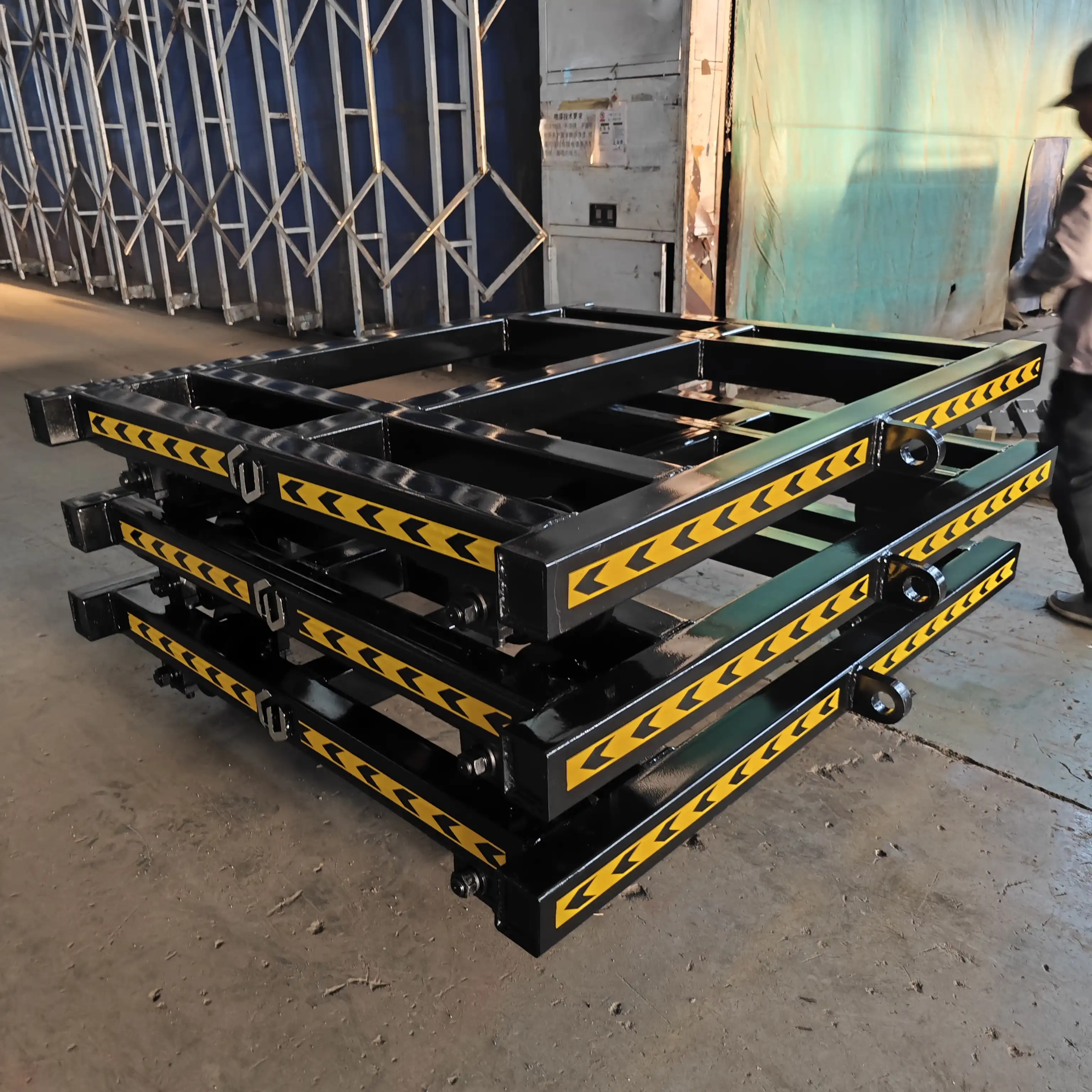
Our flagship product, the rail track trolley, is designed to meet a wide range of industrial needs. It is compatible with host machines ranging from 5 tons to 10 tons, ensuring versatility in various applications. The trolley boasts an impressive size of 1700 mm by 2000 mm, providing ample space for your operations.
One of the standout features of our Rail Track Trolley is its adaptability to different track gauges. It can accommodate track gauges of 1000 mm, 1067 mm, 1435 mm, and 1520 mm, with the added advantage of customization options to perfectly fit your specific requirements. This flexibility makes it an ideal choice for diverse railway systems.
The trolley has a robust load capacity of less than 30 tons, allowing it to handle heavy loads with ease. It is equipped with four high-quality wheels, each meticulously crafted to ensure smooth and reliable movement along the tracks. The frame is constructed from durable Q355 material, while the wheels are made of premium 40Cr material, guaranteeing longevity and performance in even the most demanding conditions.
At Tiannuo Machinery, we are committed to providing you with top-notch products and services. We look forward to working with you and helping you achieve your goals.
References
[1] Schlake, B. W., Barkan, C. P., & Edwards, J. R. (2011). Train delay and economic impact analysis of in-service failures of railroad rolling stock. Transportation Research Record, 2261(1), 124-133.
[2] Iwnicki, S. (Ed.). (2006). Handbook of railway vehicle dynamics. CRC press.
[3] Profillidis, V. A. (2014). Railway management and engineering. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.
[4] Bosso, N., Gugliotta, A., & Somà, A. (2014). Multibody simulation of a freight bogie with friction dampers. ASME J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn.
[5] Sun, Y. Q., & Cole, C. (2007). Vertical dynamic behavior of three-piece bogie suspensions with two types of friction wedge. Multibody System Dynamics, 19(4), 365-382.
[6] Pita, A. L., Teixeira, P. F., & Robusté, F. (2004). High speed and track deterioration: The role of vertical stiffness of the track. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 218(1), 31-40.