What is the mechanism of a track trolley?
A rail track trolley operates through an ingenious combination of mechanical components designed specifically for railway applications. The fundamental mechanism of a track trolley consists of specialized wheels that fit precisely onto the rails, allowing for smooth movement along the track with minimal resistance. These trolleys utilize a simple yet effective propulsion system, typically manually operated through push handles or motorized in advanced models. The core functionality relies on the strategic placement of the wheels that maintain proper alignment with the track gauge, ensuring stability during operation. Most rail trolleys incorporate essential safety features, such as braking mechanisms that provide operators with control over movement and stopping capabilities. The platform or deck serves as the functional surface for transporting maintenance tools, equipment, or personnel. This basic mechanical design has proven remarkably effective for railway maintenance operations, offering a balance of mobility, stability, and load-bearing capacity that makes the rail trolley an indispensable tool for railway maintenance crews worldwide.
Wheels and Braking Mechanism
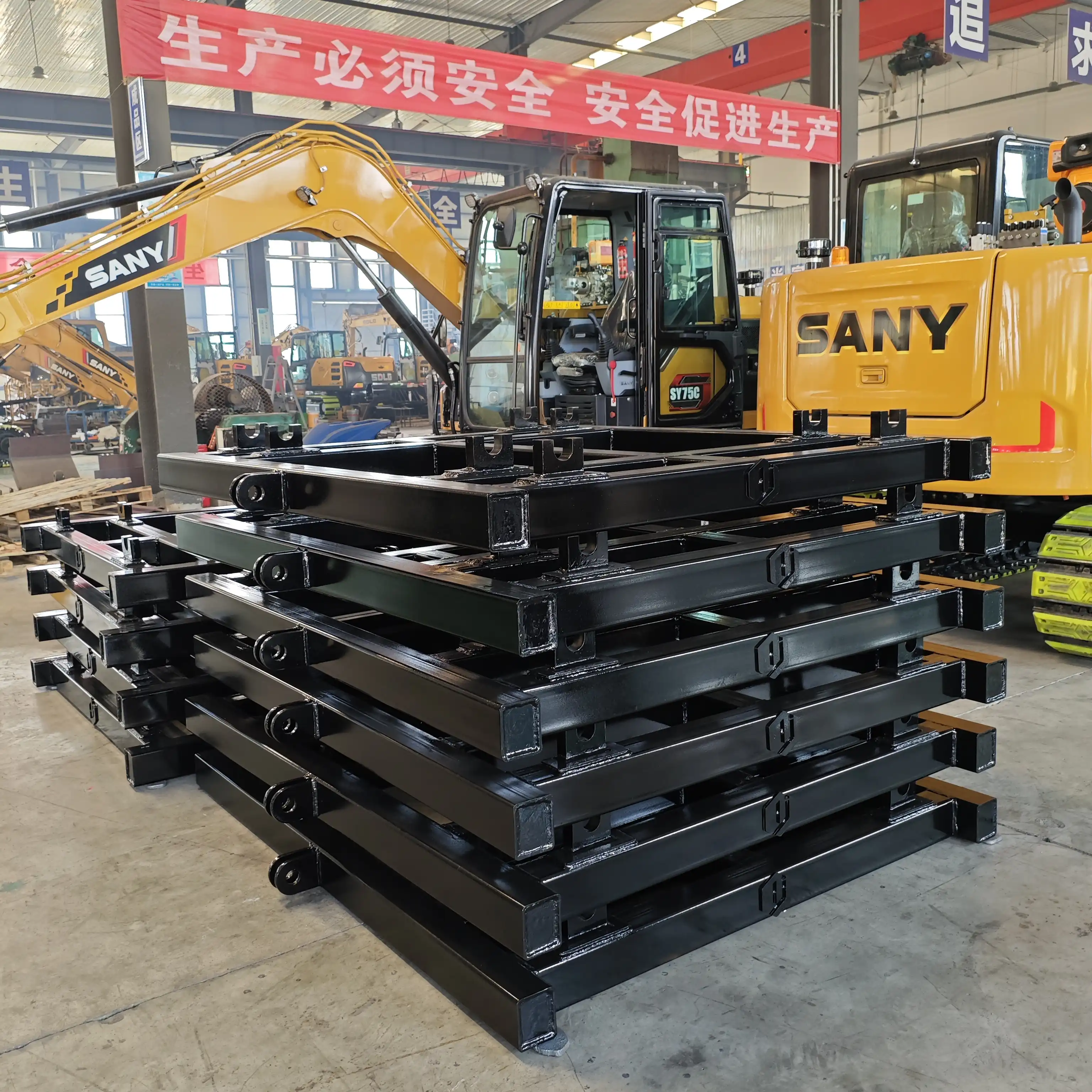

Wheel Design and Railway Interface
The wheels of a rail track trolley represent a masterful engineering solution to the challenge of railway maintenance mobility. Unlike conventional wheels, trolley wheels feature a distinctive flanged design with a slightly conical running surface and an inner flange that prevents derailment by keeping the trolley securely on the track. These wheels are typically manufactured from high-strength steel alloys that provide exceptional durability against the continuous metal-on-metal contact with rails. The precise dimensional specifications of these wheels ensure compatibility with standard railway gauges worldwide, typically ranging between 1,435mm for standard gauge and various measurements for narrow or broad gauge applications. The wheel design incorporates tapered profiles that facilitate smooth negotiation of curves without excessive friction or binding, allowing maintenance crews to navigate complex track geometries efficiently.
The interface between the wheels and the rails demonstrates remarkable engineering precision. The contact area between wheel and rail is surprisingly small—approximately the size of a dime—yet capable of supporting substantial loads due to the distribution of forces. This contact point shifts slightly as the trolley navigates curves, utilizing principles of differential rolling to minimize slippage and wear. The wheels' metallurgical composition offers an optimal balance between hardness (to resist wear) and toughness (to prevent fracture), ensuring operational longevity under diverse environmental conditions. Many advanced rail track trolleys feature sealed precision bearings that reduce rolling resistance and maintenance requirements, allowing for smoother operation even when transporting heavy equipment along extended track sections.
Braking System Components and Operation
The braking mechanism of a rail track trolley incorporates multiple components working in synchronized harmony to provide reliable stopping power in various operational scenarios. The primary braking system typically utilizes a mechanical linkage that transmits force from a hand lever or foot pedal to brake shoes that contact directly with the wheels or dedicated brake drums. This mechanical advantage allows operators to generate sufficient braking force with minimal physical effort. Most trolleys implement a dual-action braking system that applies pressure to both sides of the wheel simultaneously, ensuring balanced stopping power without uneven wear patterns. The brake shoes themselves are composed of composite materials formulated to provide optimal friction coefficients against steel without causing excessive wear to either surface.
Weight Distribution and Load-Bearing Capacity
The engineering principles behind a trolley's weight distribution significantly impact its operational stability and performance on railway tracks. The center of gravity is deliberately positioned low within the trolley's frame, minimizing tipping risk when navigating uneven track sections or carrying asymmetrical loads. The axle placement and wheel spacing are precisely calculated to distribute weight evenly across all contact points, preventing excessive rail wear and ensuring predictable handling characteristics. Most professional-grade rail track trolleys feature adjustable suspension components that maintain optimal wheel contact regardless of load configuration or track irregularities.
Push Handle
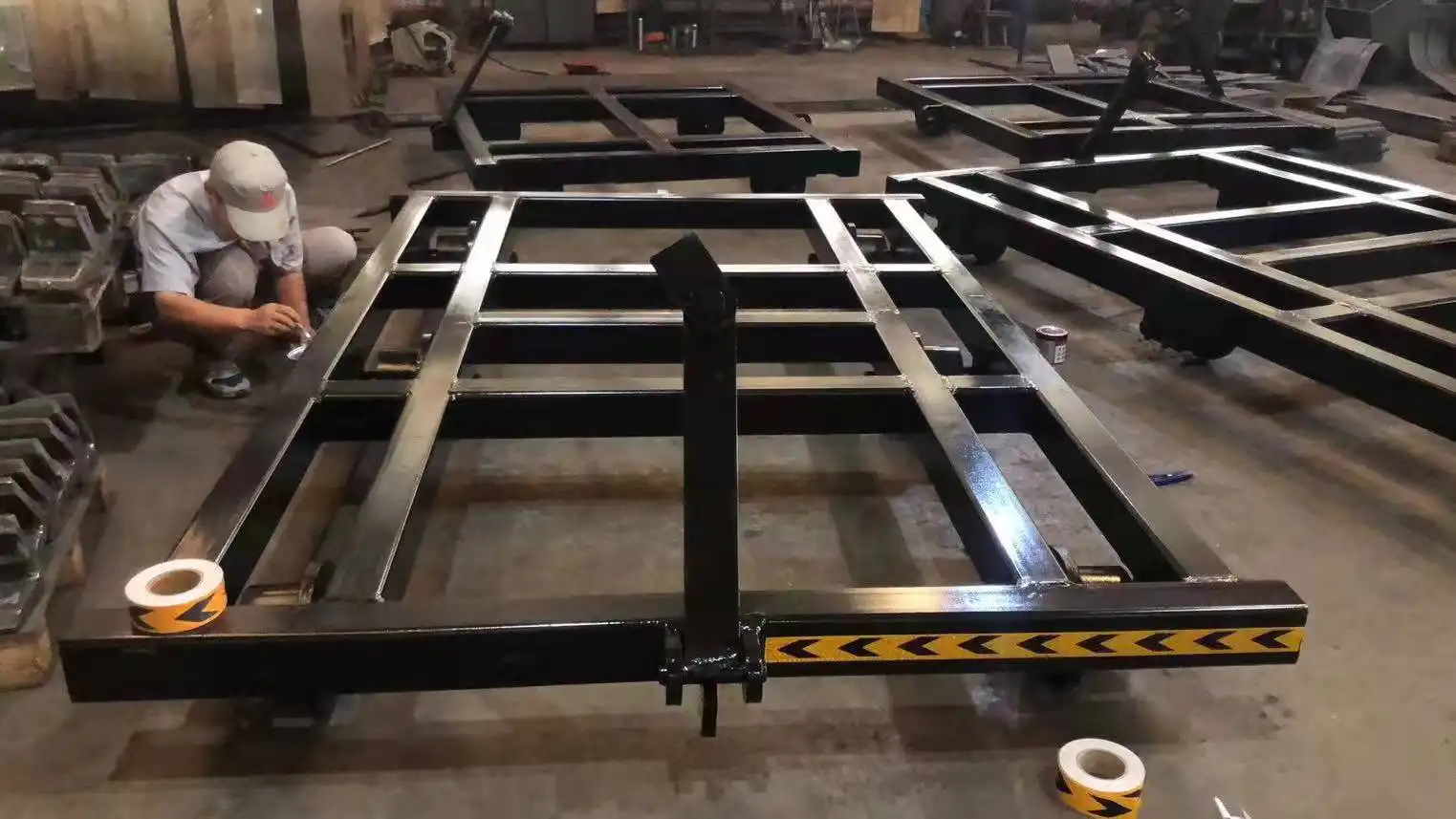

Wheel-to-Rail Interface and Grip Mechanics
The critical interaction between trolley wheels and railway tracks represents a fascinating application of tribological principles—the science of interacting surfaces in relative motion. The wheel profile features subtle contouring that maximizes contact area without increasing rolling resistance, creating an optimal balance between grip and efficiency. This precision engineering allows trolleys to maintain secure tracking even when traversing switches, crossovers, or other complex track features. The metallurgical composition of both wheels and rails creates a micro-adhesion effect at the contact point, where momentary molecular bonding occurs during the rolling process, enhancing grip without increasing friction.
Environmental factors significantly influence the wheel-rail interface, with most rail track trolleys designed to maintain performance across diverse conditions. The wheel flange depth provides sufficient safety margin to prevent derailment even when encountering minor track irregularities or debris. Advanced wheel designs incorporate self-cleaning features that continuously shed accumulated contaminants that might otherwise compromise grip or tracking precision. The interaction between wheel tread and rail surface creates a self-guiding effect that naturally maintains proper alignment even on curved sections. For enhanced traction in challenging conditions, some specialized trolleys feature composite wheel materials with optimized friction coefficients for specific applications, such as steep gradients or frequently wet environments.
Directional Control and Maneuverability
The directional control system of a rail track trolley demonstrates sophisticated engineering that balances stability with maneuverability requirements. Unlike road vehicles that require complex steering mechanisms, track trolleys rely on the inherent guidance provided by the rail-wheel interface, simplifying operation while ensuring precise tracking. The trolley's wheelbase length is carefully calibrated to provide stability during straight-line travel while still allowing smooth negotiation of curved track sections. This dimensional optimization prevents binding or excessive flange contact during cornering, reducing wear and operator effort.
Specialized design features enhance maneuverability in complex track environments. The weight distribution and center of gravity placement allow for smooth transitions between different track segments without excessive pitching or rolling motions. Many professional models incorporate swivel couplings or articulated frames that improve flexibility when navigating complex yard layouts or maintenance facilities. For operations requiring precise positioning, advanced trolleys feature incremental movement controls that allow operators to adjust position with millimeter-level precision when aligning with specific track components requiring inspection or repair. The balanced design ensures consistent handling characteristics regardless of load condition, providing predictable response to operator input even when carrying asymmetrically distributed maintenance equipment.
Deck/Platform
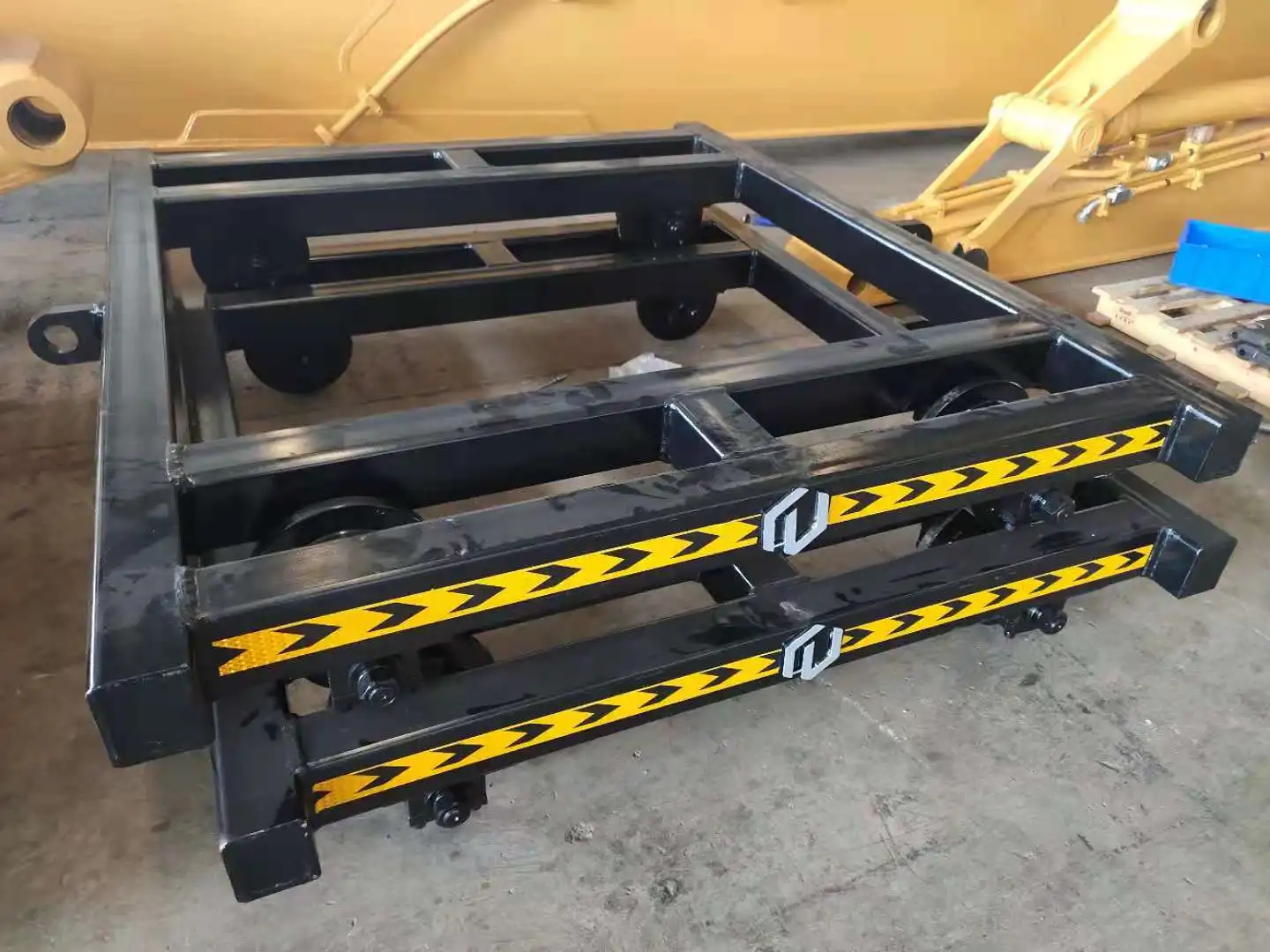

Platform Design and Material Considerations
The platform component of a rail track trolley represents a critical interface between the mechanical transport system and its practical application in railway maintenance scenarios. Platform design incorporates specialized materials selected for their optimal combination of strength, weight, and durability in demanding railway environments. High-grade aluminum alloys provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios that maximize cargo capacity without increasing propulsion requirements. Alternatively, reinforced composite materials offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical insulation properties for specialized applications involving electrical systems maintenance. For heavy-duty applications, precision-engineered steel platforms with strategic reinforcement points provide maximum load capacity while maintaining structural integrity over extended service lifespans.
The platform surface incorporates thoughtful design elements that enhance functionality during diverse maintenance operations. Non-slip textured surfaces provide secure footing and cargo stability during movement or while working on the stationary trolley. Many professional models feature integrated drainage channels that prevent water accumulation during outdoor operations, maintaining safe working conditions regardless of weather conditions. The platform perimeter often includes standardized attachment points for securing cargo straps, specialized tool holders, or safety railings when transporting personnel. Advanced designs incorporate modular platform sections that can be reconfigured based on specific maintenance tasks, maximizing versatility from a single trolley investment. The platform-to-frame connection utilizes vibration-isolating mounts that protect sensitive equipment from track-induced vibrations while maintaining structural rigidity under load.
Load Securement and Customization Options
Effective load management represents a fundamental requirement for safe and efficient railway maintenance operations using track trolleys. Professional-grade models incorporate comprehensive securement systems that prevent load shifting during movement or when working on inclined track sections. Strategically positioned tie-down points feature reinforced anchor points integrated directly into the trolley's structural frame rather than merely attached to the platform surface. These engineered attachment points provide secure anchoring for specialized straps, chains, or purpose-designed clamps that maintain precise equipment positioning throughout transport operations. The securement system design accommodates various load shapes and weight distributions while providing quick release capabilities for efficient deployment at the worksite.
The customization capabilities of modern rail track trolleys demonstrate remarkable versatility across diverse maintenance requirements. Modular accessory systems allow maintenance departments to configure trolleys for specific operational needs without requiring multiple specialized units. Available accessories include adjustable tool organizers that maximize accessibility while minimizing platform footprint, specialized cradles for transporting rail sections or ties, and collapsible weather protection systems for sensitive equipment or electronics. Many manufacturers offer industry-specific configurations optimized for signal maintenance, track inspection, catenary service, or tunnel operations. For organizations with unique requirements, custom platform configurations can incorporate specialized fixtures, power distribution systems, or integrated storage compartments designed around specific tool inventories or operational protocols.
FAQ
1. How much weight can a typical rail track trolley support?
Standard industrial rail track trolleys typically support between 500-2,000 pounds (225-900 kg), though specialized heavy-duty models can handle significantly higher capacities ranging from 3,000-10,000 pounds (1,360-4,500 kg).
2. What maintenance does a rail track trolley require?
Proper maintenance of a rail track trolley involves regular inspection of critical components including wheel flanges for wear patterns or damage, bearing lubrication to prevent seizing, brake system adjustment to maintain stopping performance, and structural frame examination for any signs of stress or fatigue.
3 . Can rail track trolleys operate on any type of rail system?
Rail track trolleys are engineered for specific track gauges and cannot operate interchangeably between different rail systems without appropriate modifications. Standard gauge trolleys (1,435mm) represent the most common configuration but cannot function on narrow gauge or broad gauge railways.
Contact Tiannuo
The mechanism of a rail trolley represents a perfect example of purpose-driven engineering that continues to serve as a cornerstone of efficient railway maintenance operations worldwide. The carefully integrated systems—from specialized wheel designs to ergonomic control interfaces—work in harmonious coordination to provide safe, reliable transport capabilities in challenging railway environments. The enduring presence of these trolleys in modern maintenance operations testifies to their exceptional utility and adaptability across evolving railway technologies and maintenance methodologies.
For organizations seeking high-quality railway maintenance equipment, including track trolleys and specialized attachments, Tiannuo Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. offers comprehensive solutions backed by extensive industry experience. Our engineering team specializes in designing and manufacturing premium railway maintenance equipment suited to diverse operational requirements and environmental conditions. To learn more about our rail track trolley options or discuss customized solutions for your specific maintenance challenges, please contact us at arm@stnd-machinery.com, rich@stnd-machinery.com, and tn@stnd-machinery.com.
References
Johnson, P.T. (2023). Railway Maintenance Equipment: Engineering Principles and Applications. Railway Engineering Press.
Zhang, L. & Thompson, D.J. (2022). Track Maintenance Vehicles: Design, Operation and Safety. International Journal of Railway Technology, 11(3), 45-62.
National Railway Safety Board. (2023). Safety Standards for Track Maintenance Equipment. Technical Publication Series 2023-05.
Wilson, M.R. (2023). Manual of Railway Engineering Standards: Track Maintenance Equipment. American Railway Engineering Association.
Patel, S. & Yamamoto, K. (2023). Advances in Railway Maintenance Technology: Equipment Evolution and Application. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 18(2), 112-128.
About Author: Arm
Arm is a leading expert in the field of specialized construction and railway maintenance equipment, working at Tiannuo Company.