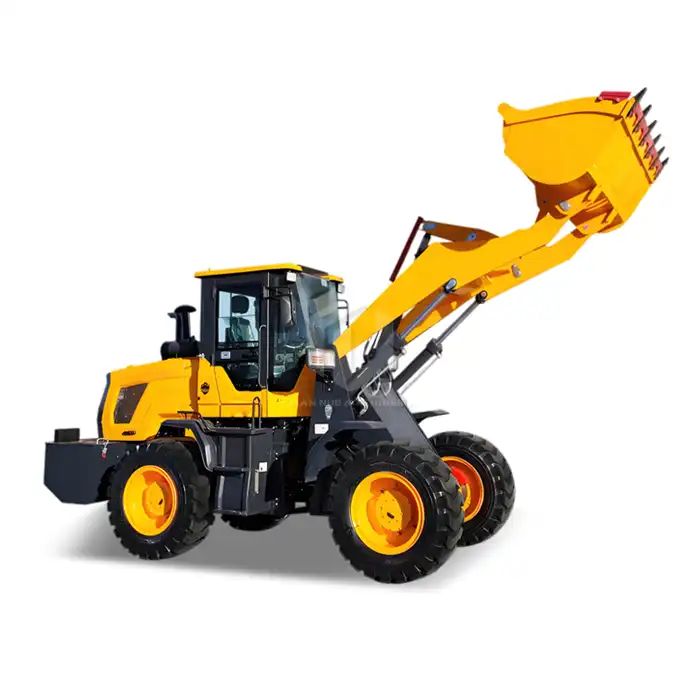
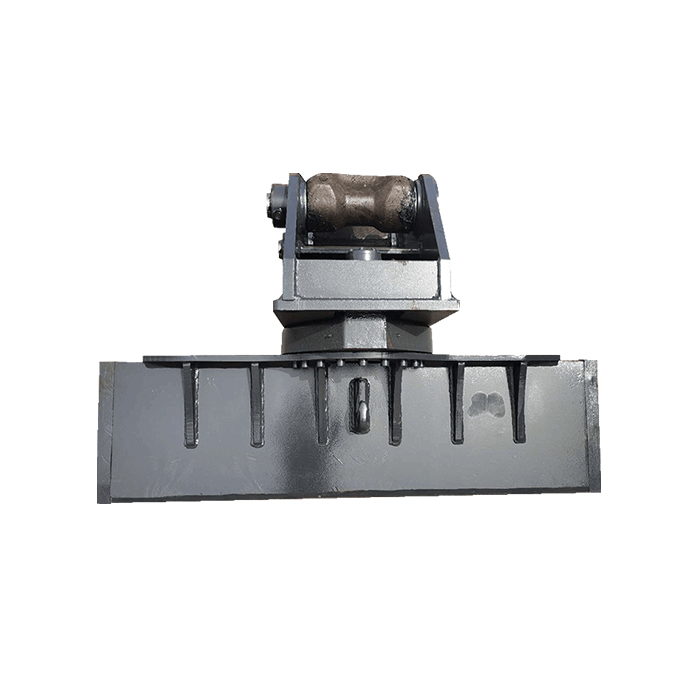
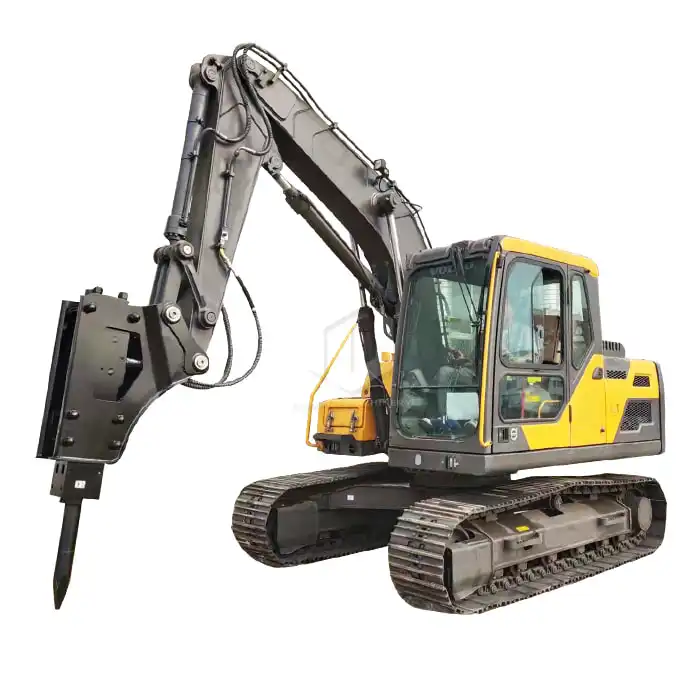
Ballast Tamper Construction
Maintaining the integrity of railway tracks requires advanced machinery, and the ballast tamper is a crucial tool in this field. This equipment, engineered for precision and efficiency, is fundamental in ensuring that railway infrastructure remains stable, safe, and durable over time. By compacting and aligning the ballast layer beneath the tracks, they help preserve the smooth operation of rail networks and support the increasing demands of modern transportation.
TianNuo Machinery takes you on a detailed exploration of ballast tampers construction, power and control systems, tamping actuators, and auxiliary structures.
Ballast Tamper Construction: Building the Foundation for Efficient Track Maintenance
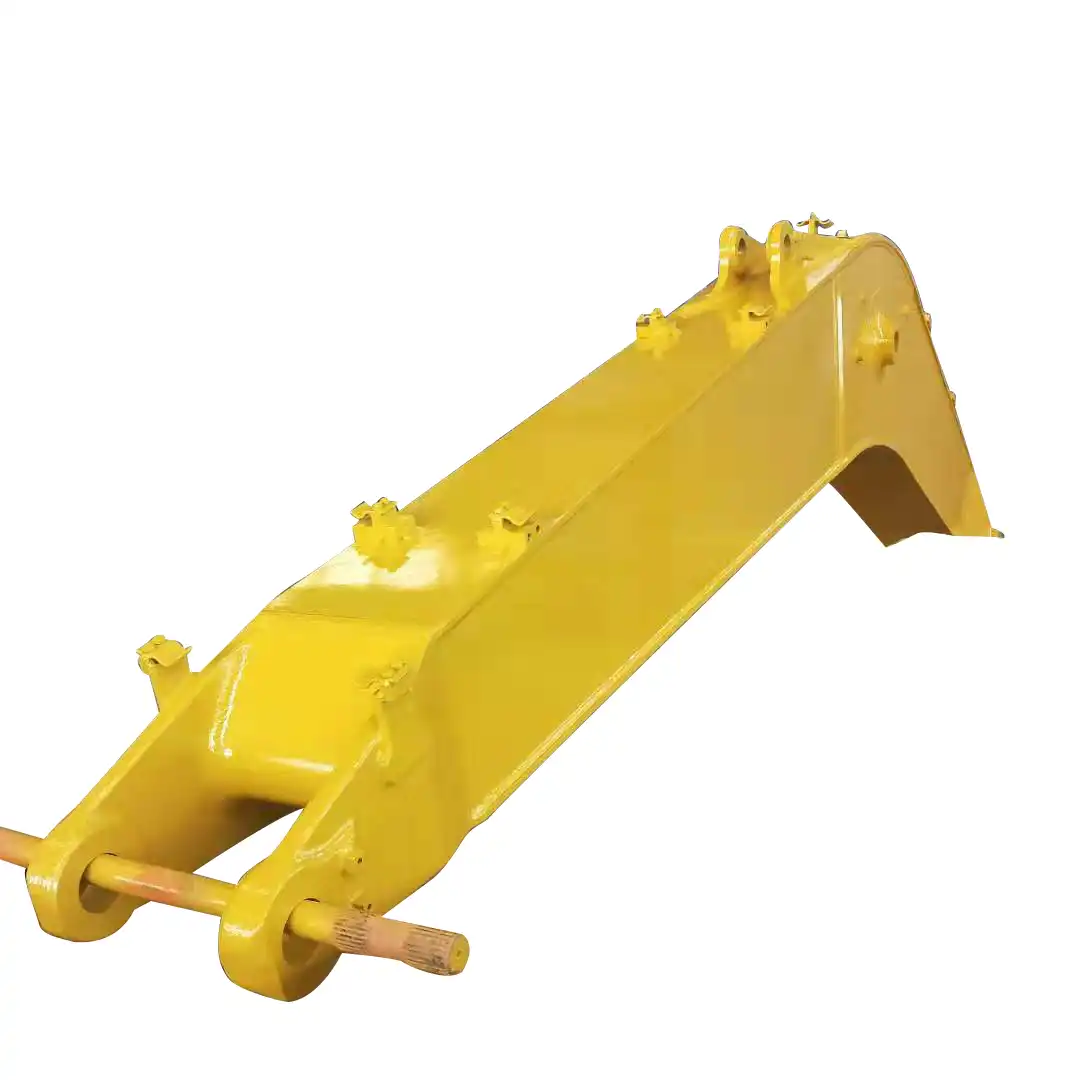
The construction of a ballast tamper is a marvel of engineering, designed to withstand the rigors of railway maintenance while delivering precise and powerful performance. At its core, it consists of a robust frame that houses the various components essential for its operation. This frame is typically mounted on railway wheels, allowing the machine to move along the tracks it's maintaining.
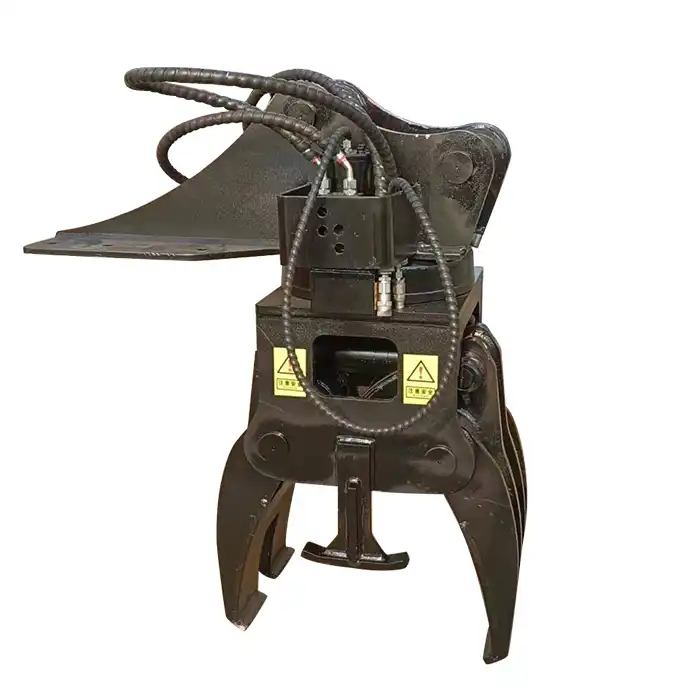
One of the most critical elements of a its construction is the tamping unit. This is where the actual work of compacting and redistributing ballast takes place. The tamping unit consists of multiple tamping tools, often referred to as "tines" or "arms," which are hydraulically or pneumatically operated. These arms are designed to penetrate the ballast layer and compact it effectively, ensuring proper support for the track structure.
The its construction also includes a sophisticated lifting and lining system. This system is responsible for adjusting the track's position both vertically and horizontally. It typically consists of rollers or clamps that can grip the rails, along with hydraulic cylinders that can apply the necessary force to move the track into the desired position.
Another crucial aspect of ballast tamper construction is the operator's cabin. Modern tampers are equipped with ergonomically designed cabins that offer excellent visibility of the work area. These cabins are often climate-controlled and feature advanced control panels and displays, allowing the operator to monitor and adjust the tamping process with precision.
The overall design of a ballast tamper also takes into account the need for mobility and versatility. Many tampers are constructed with the ability to work in both directions, eliminating the need for time-consuming turnarounds. Additionally, some models feature modular construction, allowing for easier maintenance and upgrades.
Power and Control System: The Heart and Brain of the Ballast Tamper
The power and control system of a ballast tamper is what brings this complex machine to life, enabling it to perform its critical function with precision and efficiency. At the heart of this system is a powerful engine, typically diesel-powered, which provides the necessary energy to drive all of the tamper's functions.
The engine's power is distributed through a sophisticated hydraulic system. This hydraulic system is responsible for operating the tamping units, lifting and lining mechanisms, and propulsion system. The use of hydraulics allows for smooth, controlled movements and the application of significant force where needed.
Complementing the power system is an advanced control system that serves as the "brain" of the ballast tamper. Modern tampers are equipped with computerized control systems that offer a high degree of automation and precision. These systems typically include:
- GPS and laser-guided positioning systems for accurate track alignment
- Onboard computers that store track data and calculate optimal tamping parameters
- Touch-screen interfaces for easy operation and monitoring
- Telemetry systems for remote diagnostics and performance monitoring
The control system allows for precise adjustment of tamping depth, force, and frequency, ensuring that the ballast is compacted to the ideal density for optimal track support. Many modern tampers also feature automatic cycle control, which streamlines the tamping process and improves overall efficiency.
Another critical component of the control system is the measurement and recording equipment. This includes sensors that monitor track geometry, ballast density, and machine performance. The data collected by these sensors is used to guide the tamping process and can also be stored for later analysis, helping to inform long-term track maintenance strategies.
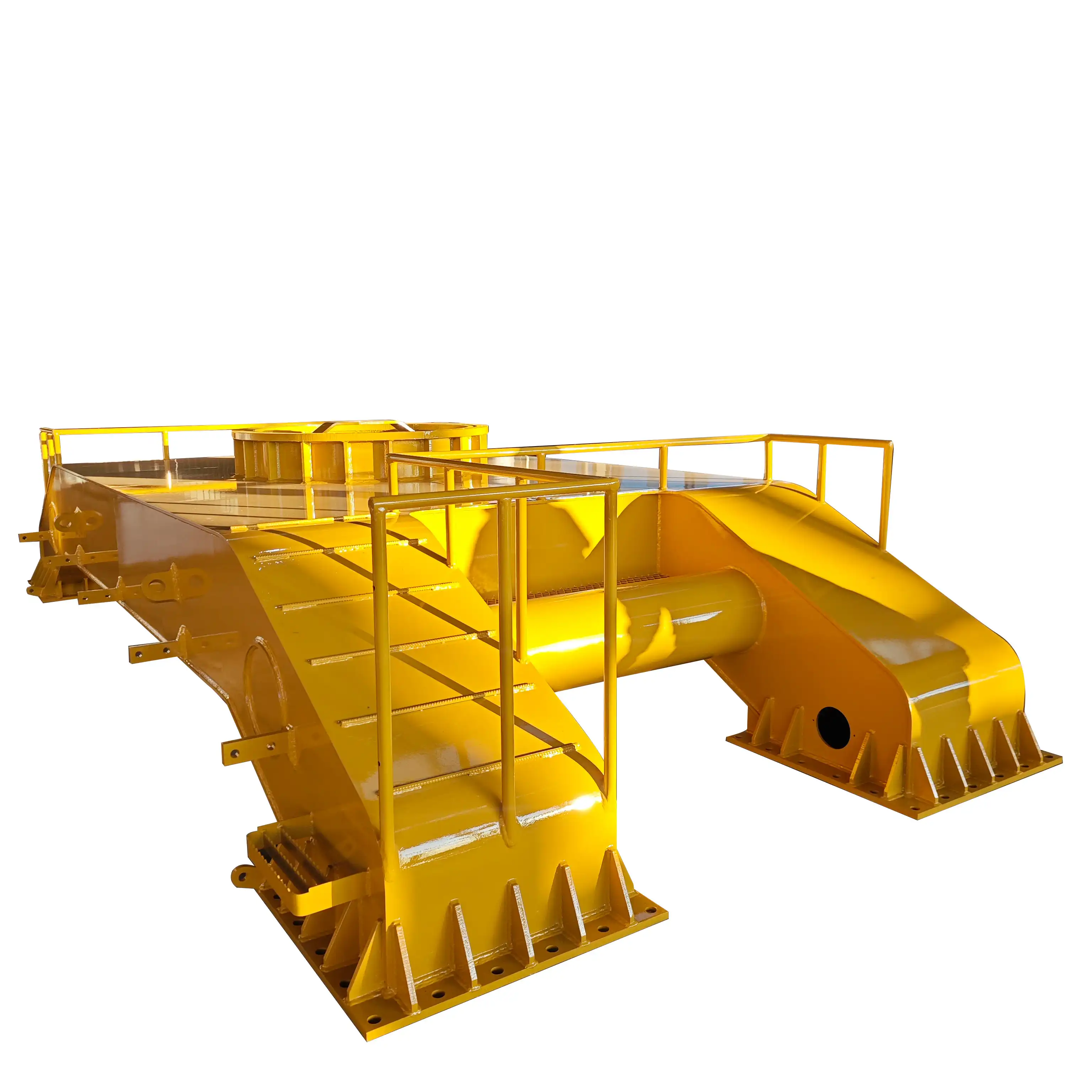
Tamping Actuator, Structure and Auxiliary Systems: Ensuring Precision and Efficiency
The tamping actuator is at the core of the ballast tamper's functionality, responsible for the actual process of compacting the ballast beneath the railway tracks. This system consists of several key components working in harmony to achieve optimal track stability.
The tamping tools, or tines, are the business end of the actuator system. These are typically made from high-strength, wear-resistant materials to withstand the rigors of repeated ballast penetration. The tines are designed to vibrate at high frequencies, allowing them to effectively "squeeze" the ballast particles together, increasing density and stability.
The actuator's structure is designed to allow for precise control of the tamping process. This includes mechanisms for adjusting the depth of penetration, the angle of the tamping tools, and the force applied during compaction. Many modern tampers feature independent control of each tamping unit, allowing for optimization of the process based on local track conditions.
Complementing the tamping actuator are various auxiliary systems that enhance the overall effectiveness of the ballast tamper. These may include:
- Ballast distribution systems that ensure an even layer of ballast before tamping
- Ballast profiling systems that shape the ballast shoulder after tamping
- Track stabilization systems that simulate train loading to settle the newly tamped track
- Dust suppression systems to minimize environmental impact during operation
The structure of the tamping actuator and its auxiliary systems is designed with both performance and maintenance in mind. Many components are modular, allowing for easy replacement or upgrades. This design philosophy extends to the entire machine, with manufacturers placing a strong emphasis on accessibility for routine maintenance and repairs.
Railroad Ballast Tamper For Sale
The ballast tamper is a testament to the ingenuity and precision engineering that goes into maintaining our railway infrastructure. From its robust construction to its sophisticated power and control systems, and from its precise tamping actuators to its efficient auxiliary systems, every aspect of the ballast tamper is designed to ensure safe, smooth, and reliable rail travel.
If you're in the market for a high-quality ballast tamper, look no further than Tiannuo Machinery. With 10 years of experience in excavator multifunctional equipment, Tiannuo Machinery offers tamping machines with a tamping clamping range of 180-700 mm, available in both four-claw and eight-claw configurations. Their expertise and commitment to quality make them an excellent choice for your railway maintenance needs.
To learn more about Tiannuo Machinery's ballast tampers or to discuss your specific requirements, don't hesitate to reach out. You can contact their manager at arm@stnd-machinery.com, or get in touch with their team at rich@stnd-machinery.com and tn@stnd-machinery.com. Take the first step towards optimizing your railway maintenance operations today!
References:
- Esveld, C. (2001). Modern railway track (Vol. 385). Zaltbommel: MRT-productions.
- Selig, E. T., & Waters, J. M. (1994). Track geotechnology and substructure management. Thomas Telford.
- Lichtberger, B. (2005). Track compendium: Formation, permanent way, maintenance, economics. Eurailpress.




_1733877348138.jpg)



